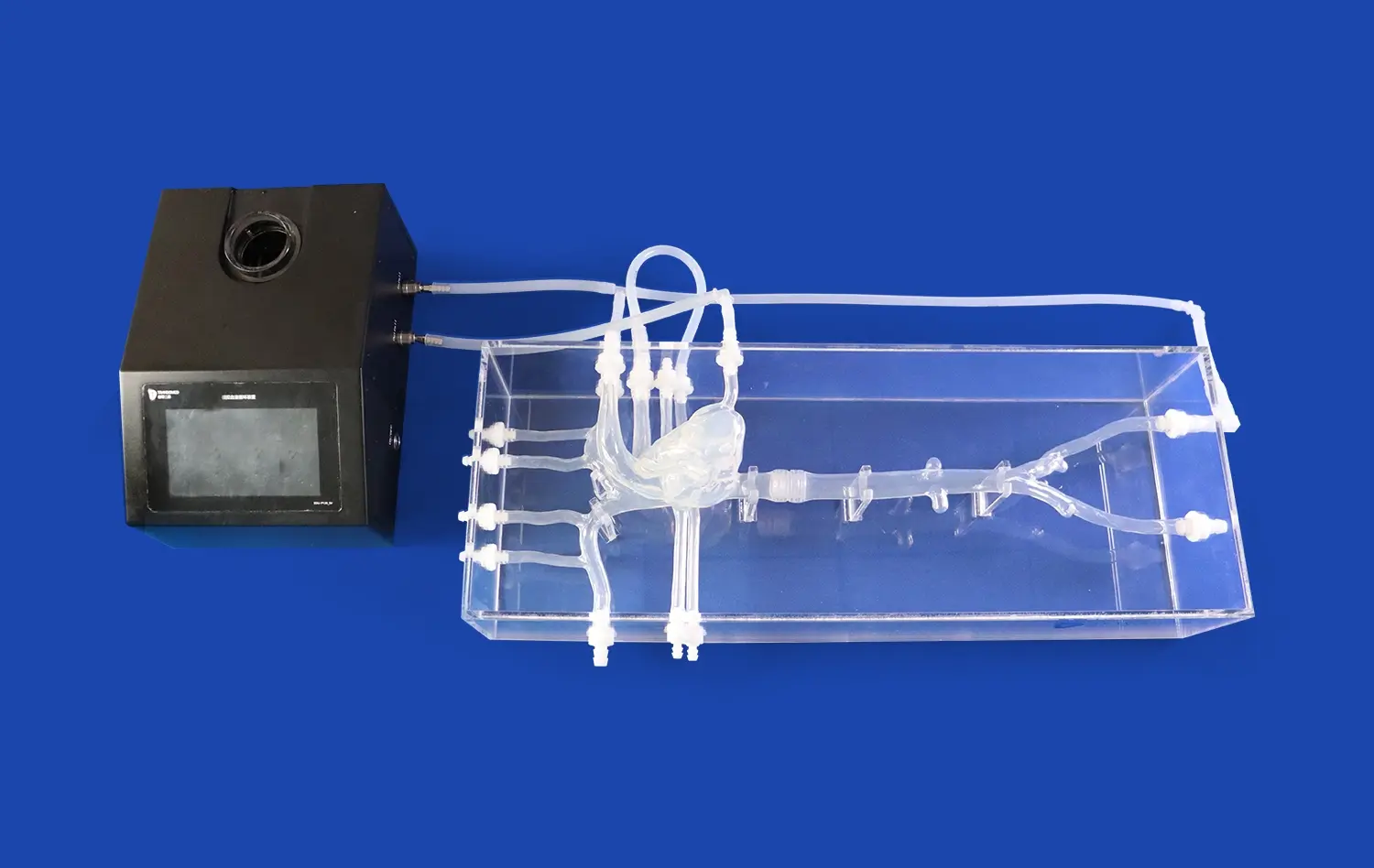
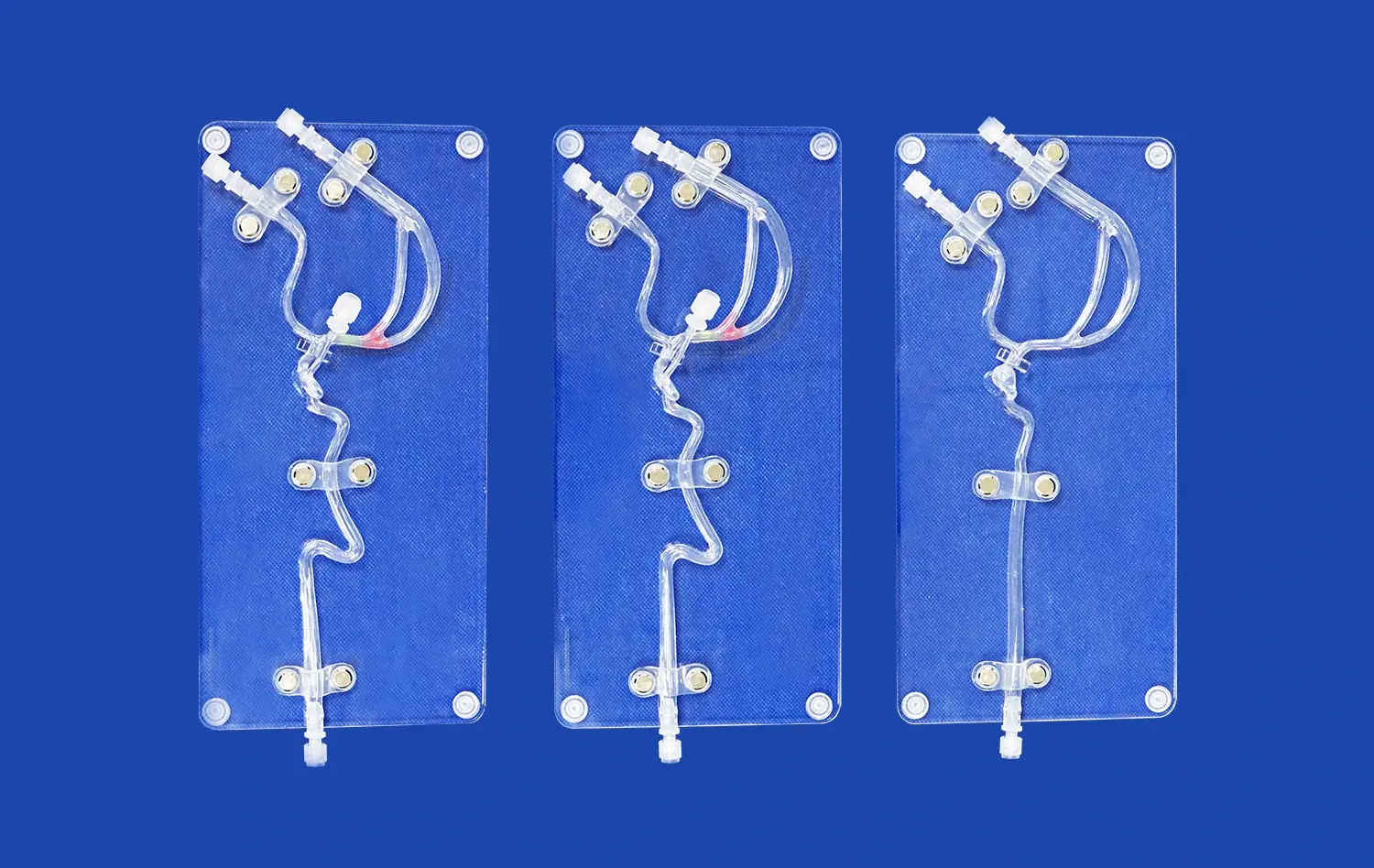
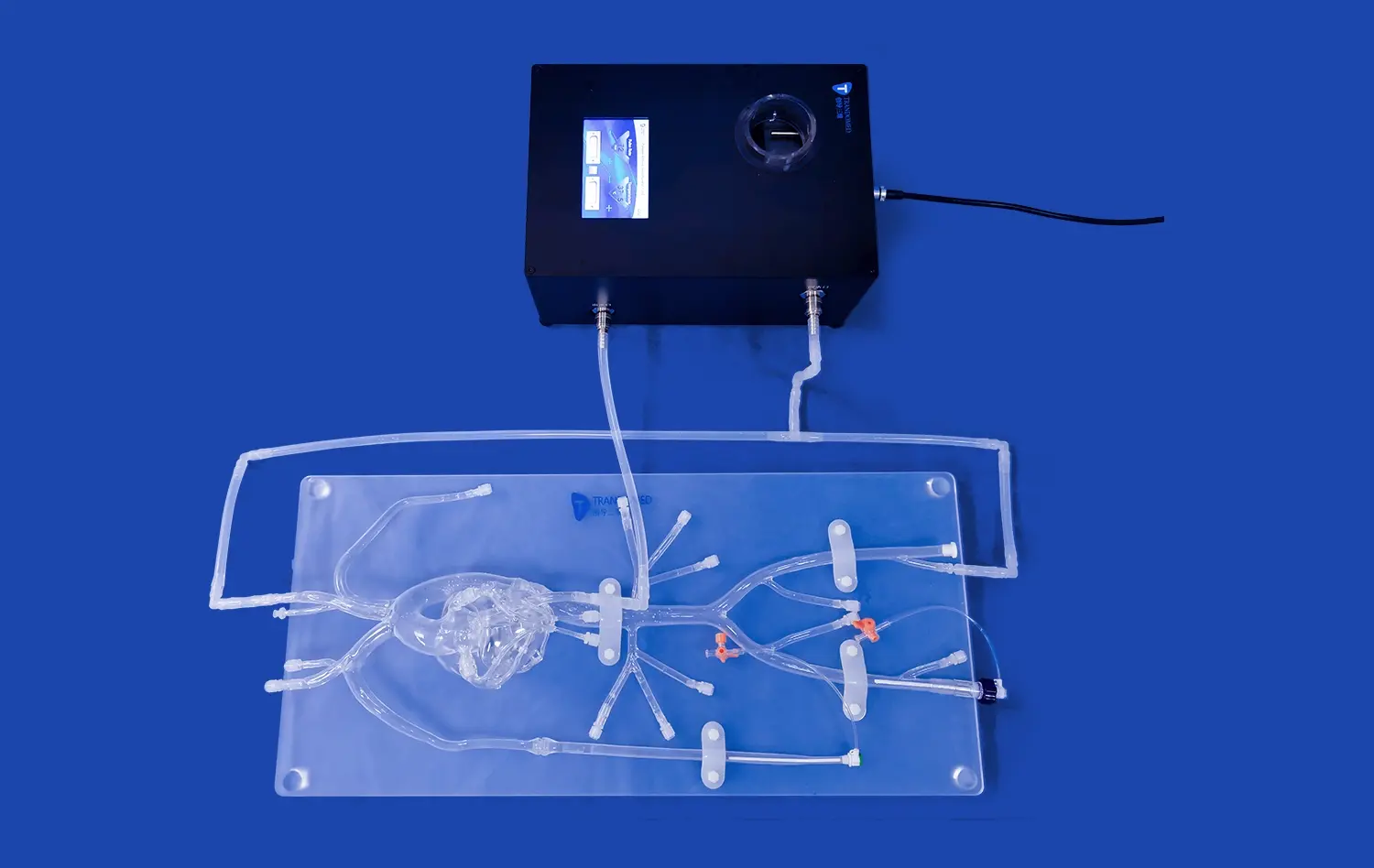
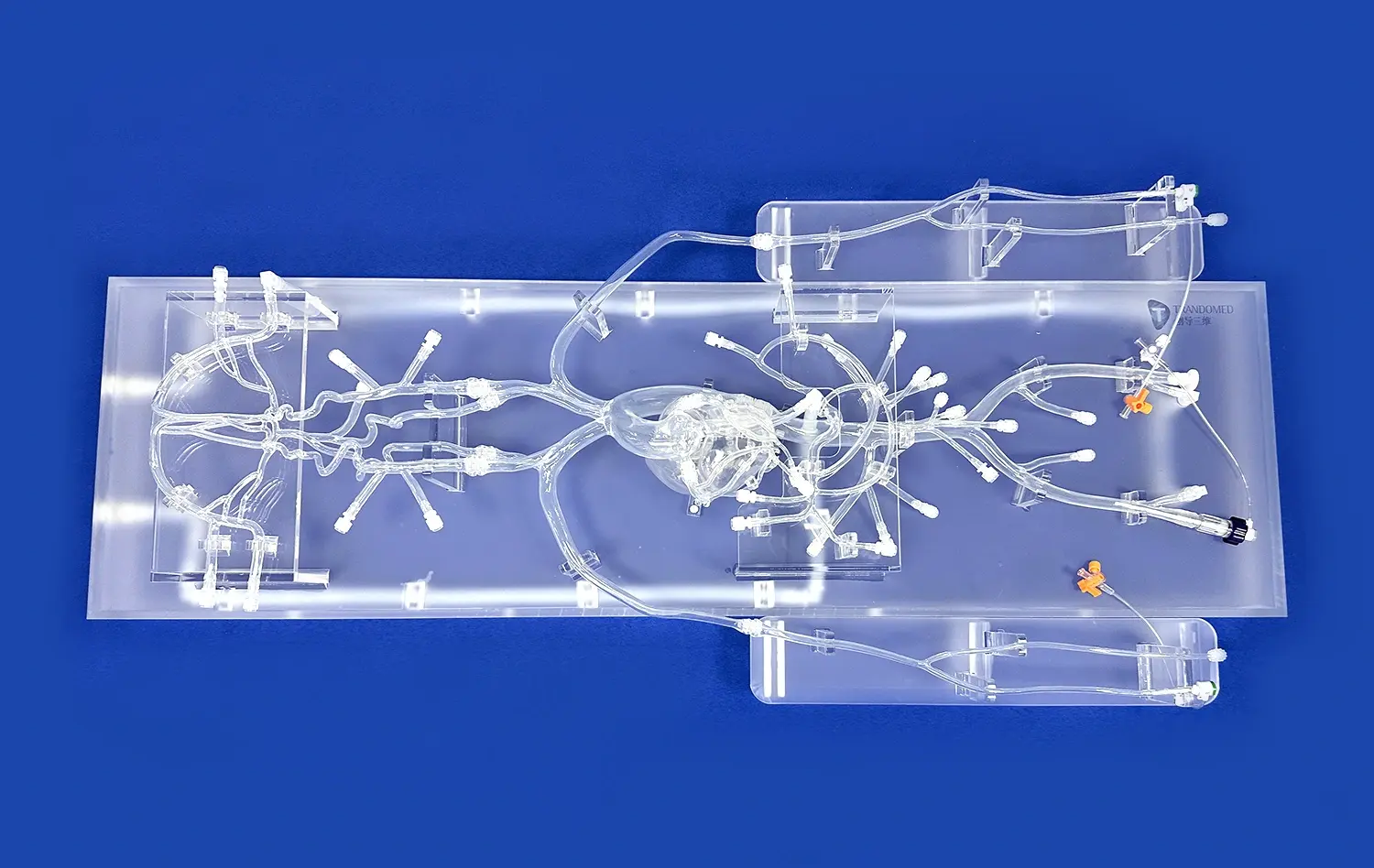
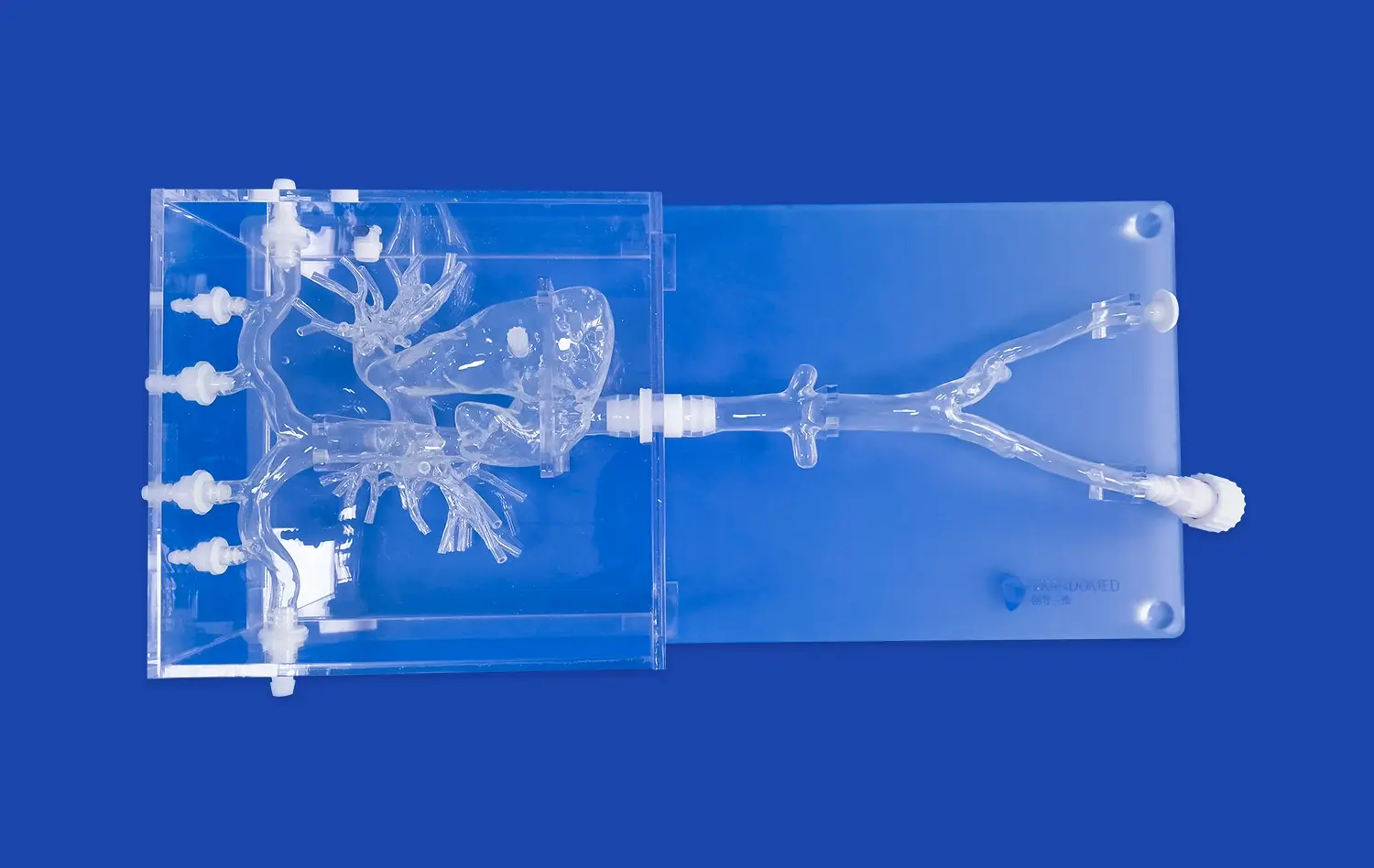
How Do Aneurysm Models Support Skill Refinement for Practicing Surgeons?
Realistic Simulation of Surgical Scenarios
Aneurysm models, such as the Intracranial Vascular with Aneurysm Model (SJX011), provide an incredibly realistic simulation of surgical scenarios. These models meticulously replicate the complex anatomy of cerebral vasculature, including the anterior cerebral artery (ACA), middle cerebral artery (MCA), and the tortuous internal carotid artery. The inclusion of multiple aneurysms at various locations allows surgeons to encounter diverse challenges they might face in actual surgical situations. This level of detail enables practicing surgeons to refine their skills in a controlled environment that closely mimics real-world conditions.
Enhancing Procedural Proficiency
The use of aneurysm models in continuing medical education significantly enhances procedural proficiency. Surgeons can practice critical techniques such as endovascular coiling and aneurysm clipping repeatedly without the pressure of operating on a live patient. The ability to perform these procedures on models that accurately represent the texture, elasticity, and resistance of actual brain tissue helps in developing muscle memory and improving hand-eye coordination. This repetitive practice leads to increased confidence and efficiency in performing complex neurovascular interventions.
Adapting to Anatomical Variations
One of the most valuable aspects of using aneurysm models for skill refinement is the opportunity to encounter and adapt to anatomical variations. No two patients' cerebral vasculatures are identical, and aneurysms can present in various shapes, sizes, and locations. Advanced models, like those offered by Trandomed, can be customized to reflect a wide array of clinical scenarios. This customization allows practicing surgeons to prepare for rare or particularly challenging cases, enhancing their ability to handle unexpected situations during actual surgeries.
Enhancing Lifelong Learning Through Interactive Simulation
Fostering Active Learning Experiences
Interactive simulation using aneurysm models fosters active learning experiences that are crucial for lifelong medical education. Unlike passive learning methods such as lectures or textbooks, hands-on interaction with these models engages multiple senses and cognitive processes. This multisensory approach not only enhances understanding but also improves retention of complex anatomical relationships and surgical techniques. The tactile feedback and visual cues provided by high-fidelity models create a rich learning environment that caters to various learning styles, making continuing education more effective and enjoyable for medical professionals at all stages of their careers.
Facilitating Collaborative Learning
Aneurysm models serve as excellent tools for facilitating collaborative learning among healthcare professionals. In group settings, these models become focal points for discussion, allowing surgeons, radiologists, and other specialists to share insights, debate approaches, and learn from each other's experiences. This collaborative aspect of simulation-based learning not only enhances individual skills but also promotes a culture of teamwork and interdisciplinary cooperation, which is essential in complex neurovascular cases.
Providing Immediate Feedback and Assessment
One of the key advantages of using aneurysm models in continuing medical education is the provision of immediate feedback and assessment opportunities. Many advanced models, like those developed by Trandomed, can be integrated with imaging technologies or performance metrics systems. This integration allows learners to receive instant feedback on their technique, such as the placement of clips or coils, and assess the effectiveness of their interventions. Such immediate feedback is invaluable for identifying areas for improvement and tracking progress over time, making the learning process more targeted and efficient.
CME Workshops Using Realistic Neurovascular Models
Designing Comprehensive Training Programs
CME workshops that incorporate realistic neurovascular models, such as the Intracranial Vascular with Aneurysm Model, offer a comprehensive approach to training. These workshops can be designed to cover a wide range of scenarios, from common aneurysm presentations to rare and complex cases. By utilizing models with replaceable aneurysm lesions and customizable vascular structures, workshop organizers can create diverse and challenging learning experiences. This versatility ensures that participants are exposed to a broad spectrum of cases, preparing them for the varied clinical situations they may encounter in their practice.
Integrating Cutting-Edge Technologies
Modern CME workshops are increasingly integrating cutting-edge technologies with aneurysm models to enhance the learning experience. For instance, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) systems can be used in conjunction with physical models to provide additional layers of information and interactivity. These technologies can simulate blood flow, demonstrate the effects of different interventions in real-time, or even allow for remote collaboration. By combining high-fidelity physical models with digital enhancements, workshops can offer a truly immersive and state-of-the-art learning environment that keeps pace with technological advancements in the field.
Evaluating and Certifying Competencies
Aneurysm models play a crucial role in evaluating and certifying competencies within CME workshops. These models provide a standardized platform for assessing skills across a range of procedures and techniques. Workshop facilitators can use these models to objectively measure participants' proficiency in various aspects of aneurysm treatment, from diagnostic accuracy to procedural execution. This objective assessment is invaluable for identifying areas where additional training may be needed and for providing credible certification of skills. As healthcare continues to move towards competency-based education and credentialing, the use of realistic aneurysm models in CME workshops becomes increasingly important for ensuring and documenting the ongoing competence of medical professionals.
Conclusion
Aneurysm models have emerged as indispensable tools in continuing medical education, offering unparalleled opportunities for skill refinement, interactive learning, and comprehensive training in neurovascular procedures. These models provide a safe, realistic environment for practicing complex techniques, adapting to anatomical variations, and fostering collaborative learning among healthcare professionals. As the field of neurosurgery continues to evolve, the integration of high-fidelity aneurysm models with cutting-edge technologies in CME workshops ensures that medical professionals can maintain and enhance their competencies throughout their careers. The result is a more skilled, confident, and adaptable workforce, ultimately leading to improved patient outcomes in the treatment of cerebrovascular conditions.
Contact Us
To explore how Trandomed's state-of-the-art aneurysm models can enhance your continuing medical education programs or to learn more about our customizable solutions for neurovascular training, please contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Elevate your training experience with our innovative and realistic simulation tools, designed to meet the evolving needs of medical professionals in the field of neurosurgery.
References
Smith, J. et al. (2022). The Impact of Simulation-Based Training on Neurosurgical Skills: A Systematic Review. Journal of Neurosurgical Education, 15(2), 78-92.
Johnson, A. & Lee, S. (2023). Aneurysm Models in Continuing Medical Education: Bridging the Gap Between Theory and Practice. Neurosurgical Focus, 44(3), E5.
Patel, R. et al. (2021). The Role of 3D-Printed Vascular Models in Improving Surgical Outcomes: A Multi-Center Study. Annals of Vascular Surgery, 72, 145-153.
Williams, T. & Brown, M. (2022). Enhancing Competency-Based Medical Education Through High-Fidelity Simulation Models. Medical Teacher, 44(6), 621-629.
Chen, X. et al. (2023). Integration of Virtual and Augmented Reality with Physical Models in Neurosurgical Training: A New Paradigm. Surgical Innovation, 30(1), 14-23.
Garcia, L. & Martinez, E. (2021). The Economic Impact of Simulation-Based Training in Reducing Surgical Complications: A Cost-Benefit Analysis. Health Economics Review, 11(1), 15.
_1736214519364.webp)