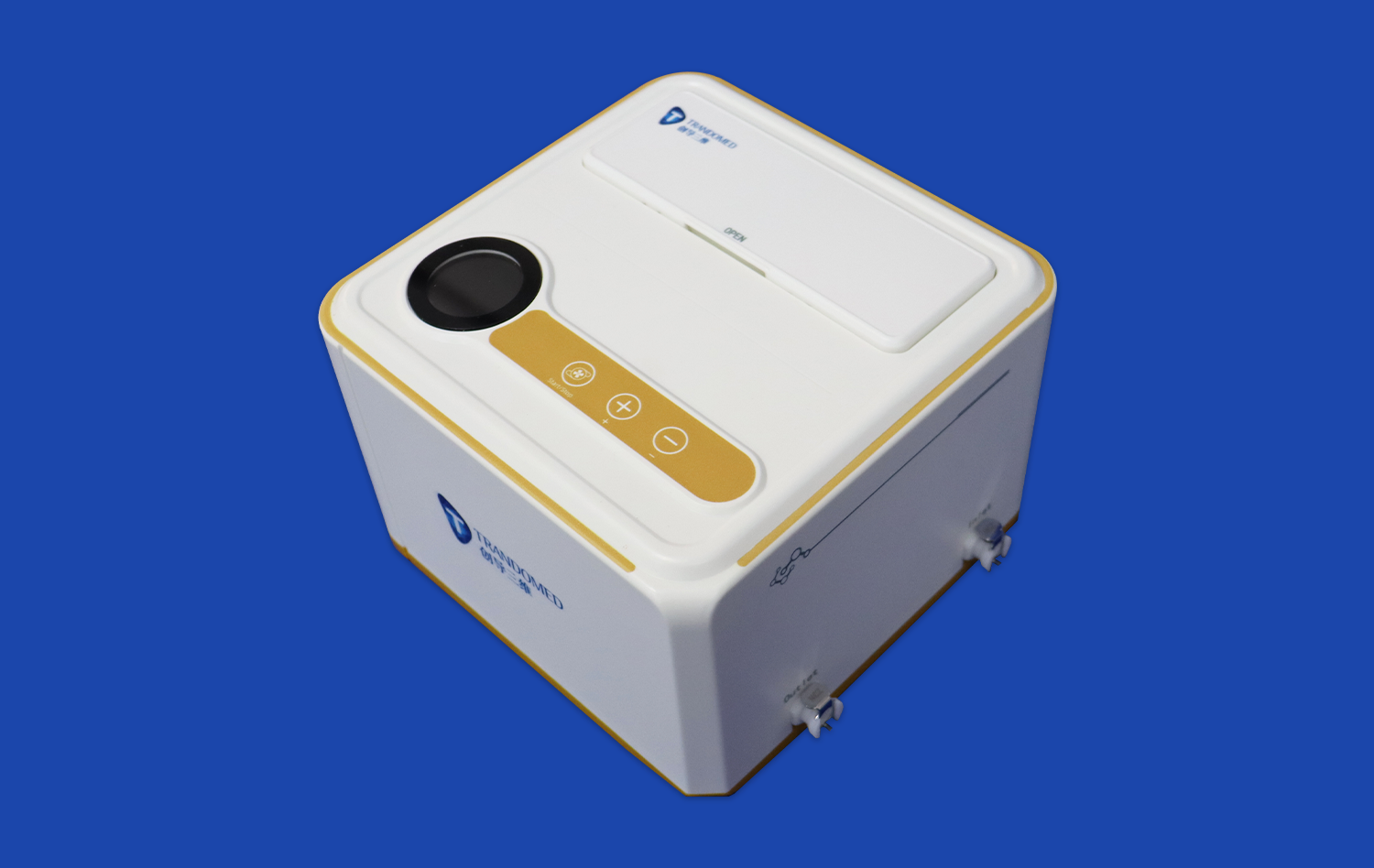
How Does the Model Minimize Risks Compared to Real Patients?
Elimination of Patient-Related Complications
Atrial septal puncture models provide a safe alternative to practicing on live patients, effectively eliminating the risk of complications such as cardiac tamponade, aortic perforation, or systemic embolization. These life-threatening events, while rare, can occur during actual procedures, especially when performed by less experienced operators. By using a simulator, medical professionals can practice the delicate maneuvers required for transseptal punctures without the stress of potentially harming a patient.
Controlled Learning Environment
The model creates a controlled setting where learners can focus solely on perfecting their technique without the distractions and pressures of a clinical environment. This controlled atmosphere allows for deliberate practice, enabling practitioners to repeat challenging aspects of the procedure until they achieve mastery. The absence of time constraints typically present in real-world scenarios permits a more thorough exploration of anatomical variations and potential complications.
Error Analysis and Immediate Feedback
Unlike in real patient scenarios, mistakes made on an atrial septal puncture model can be immediately analyzed and corrected without consequences. This immediate feedback loop is crucial for rapid skill development. Instructors can pause the procedure at any point to discuss technique, highlight potential pitfalls, and demonstrate optimal approaches. This level of detailed analysis and correction is simply not possible during live procedures, where the focus must remain on patient safety and procedural success.
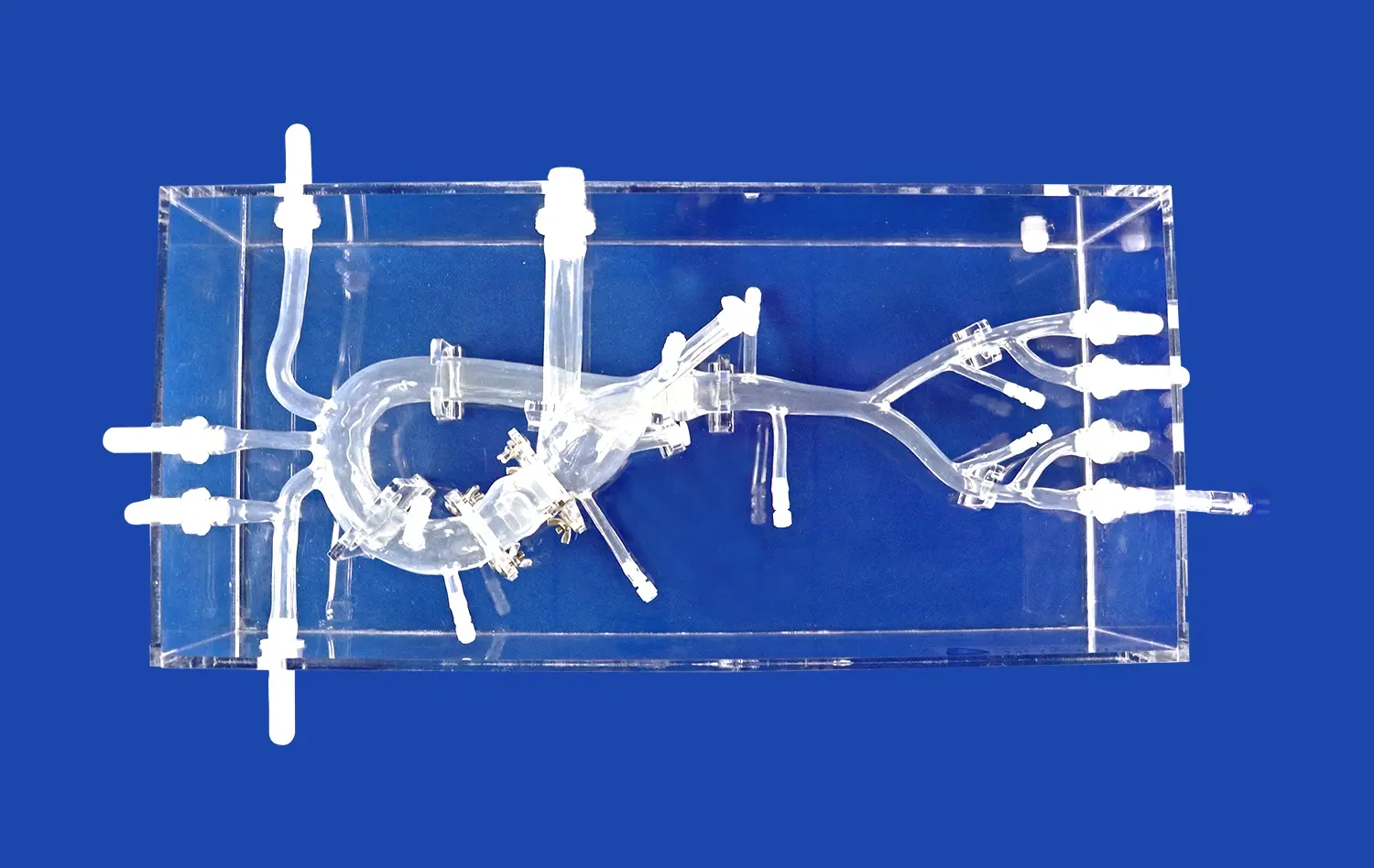
Realistic Anatomical Structures for Repeatable Practice
High-Fidelity Cardiac Anatomy
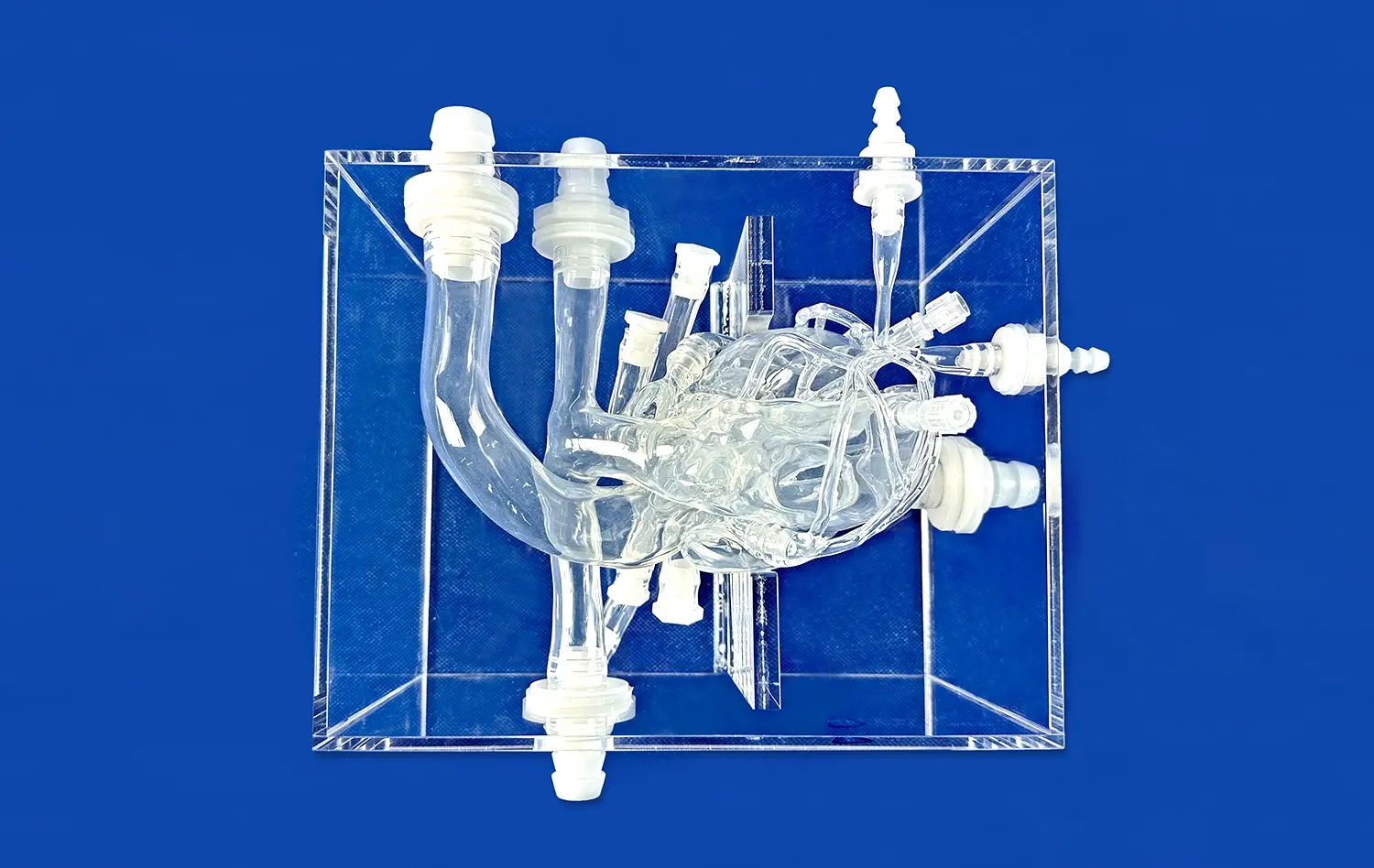
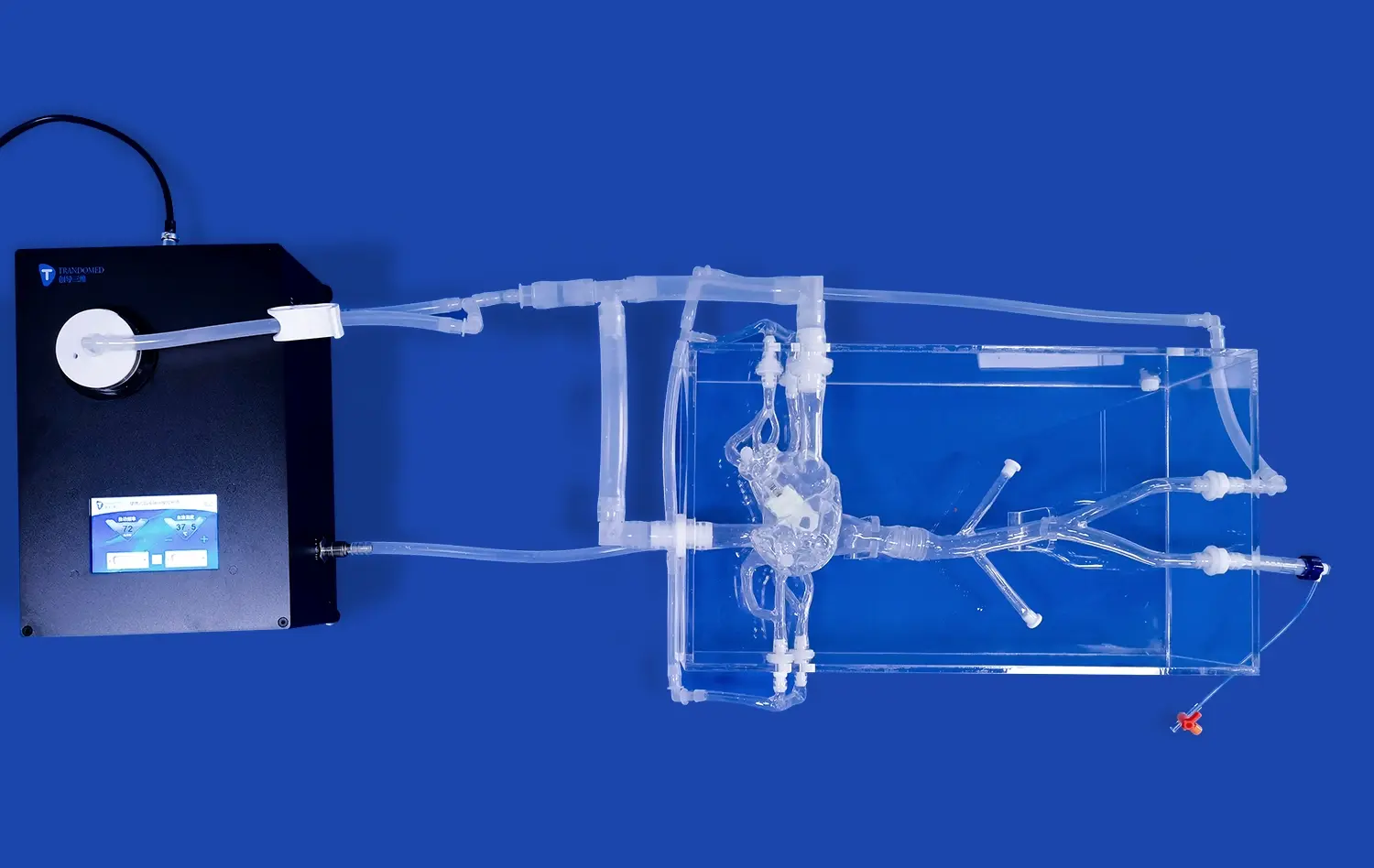
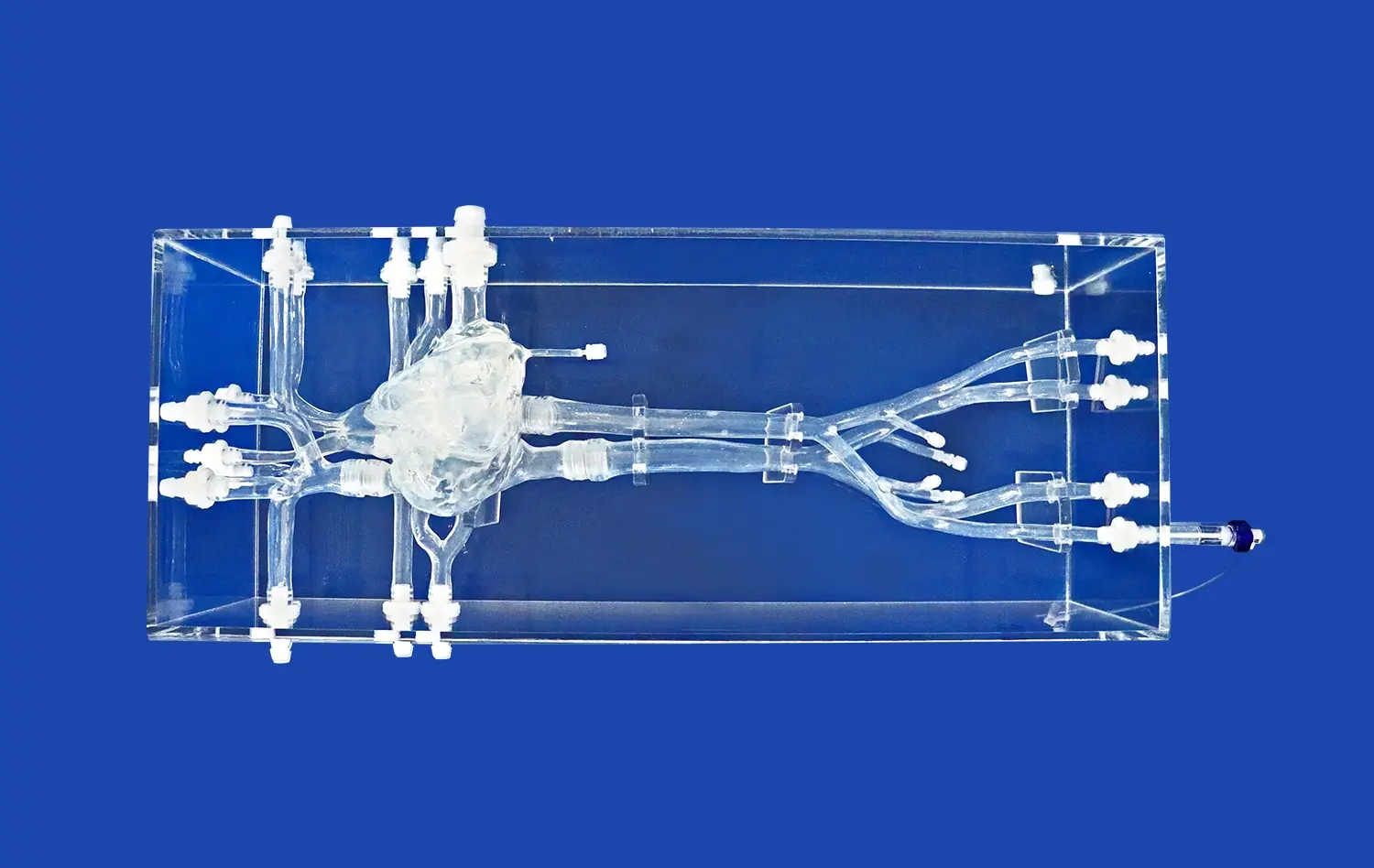
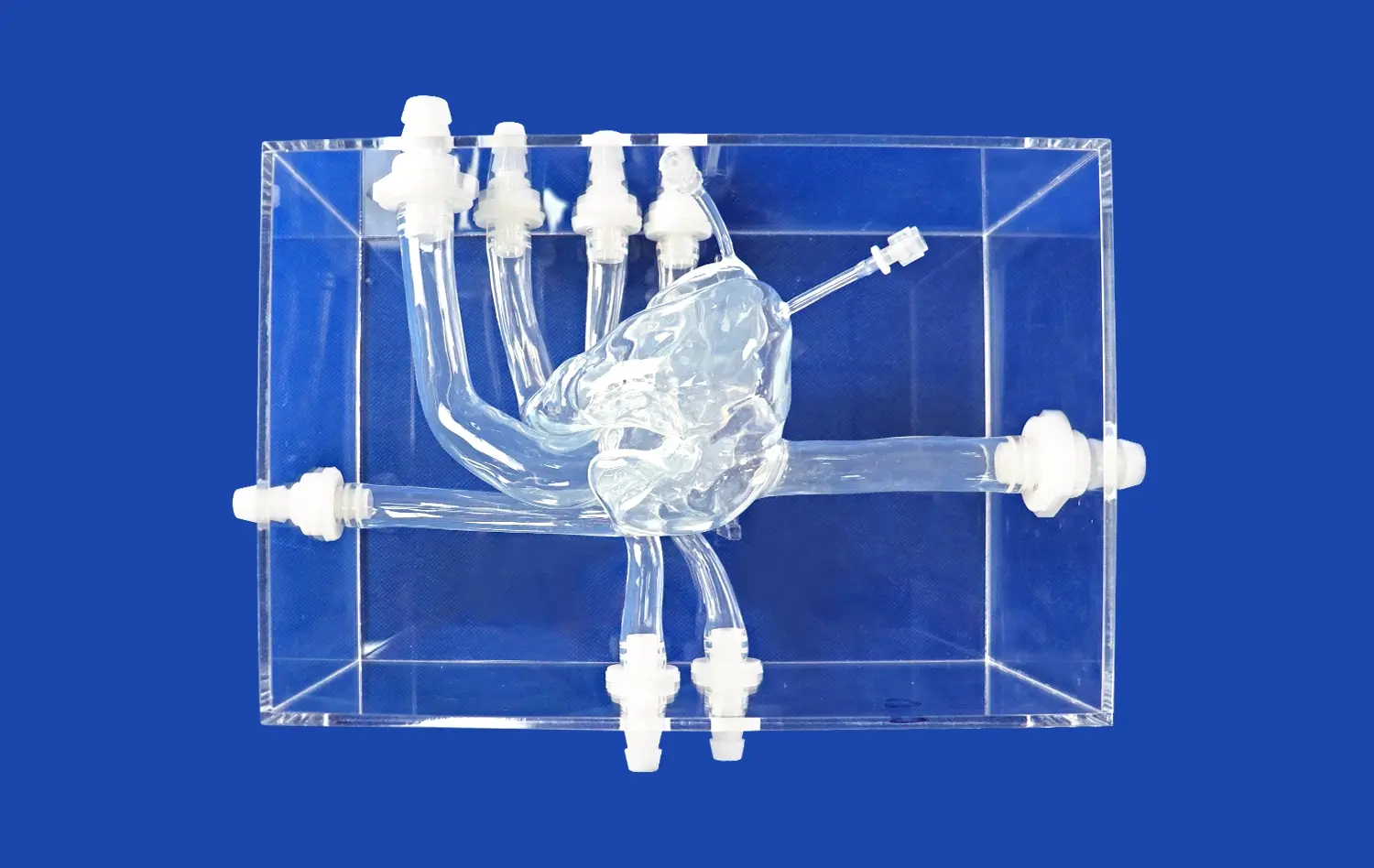
Advanced atrial septal puncture models boast remarkably accurate representations of cardiac structures. These simulators are meticulously crafted to mirror the intricate anatomy of the human heart, including the right and left atria, interatrial septum, fossa ovalis, and surrounding vessels. The high-fidelity design ensures that practitioners encounter realistic tissue resistance and tactile feedback during needle positioning and puncture, closely mimicking the sensations experienced in actual procedures.
Variability in Septal Thickness and Elasticity
Top-tier models incorporate varying degrees of septal thickness and elasticity to simulate the diverse patient populations encountered in clinical practice. This variability is crucial for developing the tactile skills necessary to safely perform transseptal punctures across a range of anatomical presentations. Practitioners can experience the subtle differences in resistance when puncturing through normal septa, thickened septa in older patients, or even previously punctured sites in repeat procedures.
Interchangeable Components for Diverse Scenarios
Many advanced atrial septal puncture simulators feature interchangeable components, allowing for the practice of various clinical scenarios. These may include normal atrial septa, atrial septal defects of different sizes, or even patent foramen ovale representations. The ability to swap out these components provides a comprehensive training experience, preparing medical professionals for the full spectrum of anatomical variations they might encounter in their practice.
Building Confidence Before Clinical Application
Graduated Learning Approach
Atrial septal puncture models facilitate a graduated learning approach, allowing medical professionals to progress from basic to advanced techniques at their own pace. Novices can begin with straightforward scenarios, focusing on proper needle placement and basic puncture technique. As they gain proficiency, learners can tackle more challenging cases, such as puncturing through thickened septa or navigating complex anatomical variations. This step-wise progression builds confidence systematically, ensuring that practitioners are well-prepared before performing procedures on actual patients.
Repetition and Muscle Memory Development
The ability to perform multiple repetitions on the atrial septal puncture model is invaluable for developing muscle memory and refining fine motor skills. Unlike in clinical settings where opportunities for practice are limited, simulators allow for countless iterations of the procedure. This repeated practice engenders a level of familiarity and comfort with the tools and techniques that translates directly to improved performance in real-world scenarios. As practitioners internalize the movements and sensations associated with successful punctures, their confidence in their abilities grows substantially.
Stress-Free Environment for Skill Mastery
One of the most significant advantages of training with an atrial septal puncture model is the stress-free environment it provides. The absence of patient-related pressure allows learners to focus entirely on perfecting their technique without the fear of causing harm. This reduced stress leads to more effective learning and faster skill acquisition. As practitioners become more comfortable with the procedure in this low-stakes setting, they develop the confidence necessary to approach real cases with a calm and composed demeanor, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes.
Conclusion
The atrial septal puncture model has become an indispensable tool in medical training, offering a safe, realistic, and effective means of honing critical cardiac intervention skills. By providing a risk-free environment for practice, these models enable medical professionals to build confidence and competence before performing procedures on actual patients. The combination of anatomical accuracy, diverse training scenarios, and the ability for repeated practice makes these simulators invaluable in modern medical education. As technology continues to advance, we can expect these models to play an increasingly crucial role in preparing the next generation of skilled interventional cardiologists.
Contact Us
For medical professionals and institutions seeking to enhance their training programs with state-of-the-art atrial septal puncture models, Trandomed offers cutting-edge solutions backed by years of expertise in medical simulation technology. Our models, crafted with precision using advanced 3D printing techniques and high-quality materials, provide unparalleled realism and durability. To explore how our atrial septal puncture simulators can elevate your training experience and improve patient outcomes, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com.