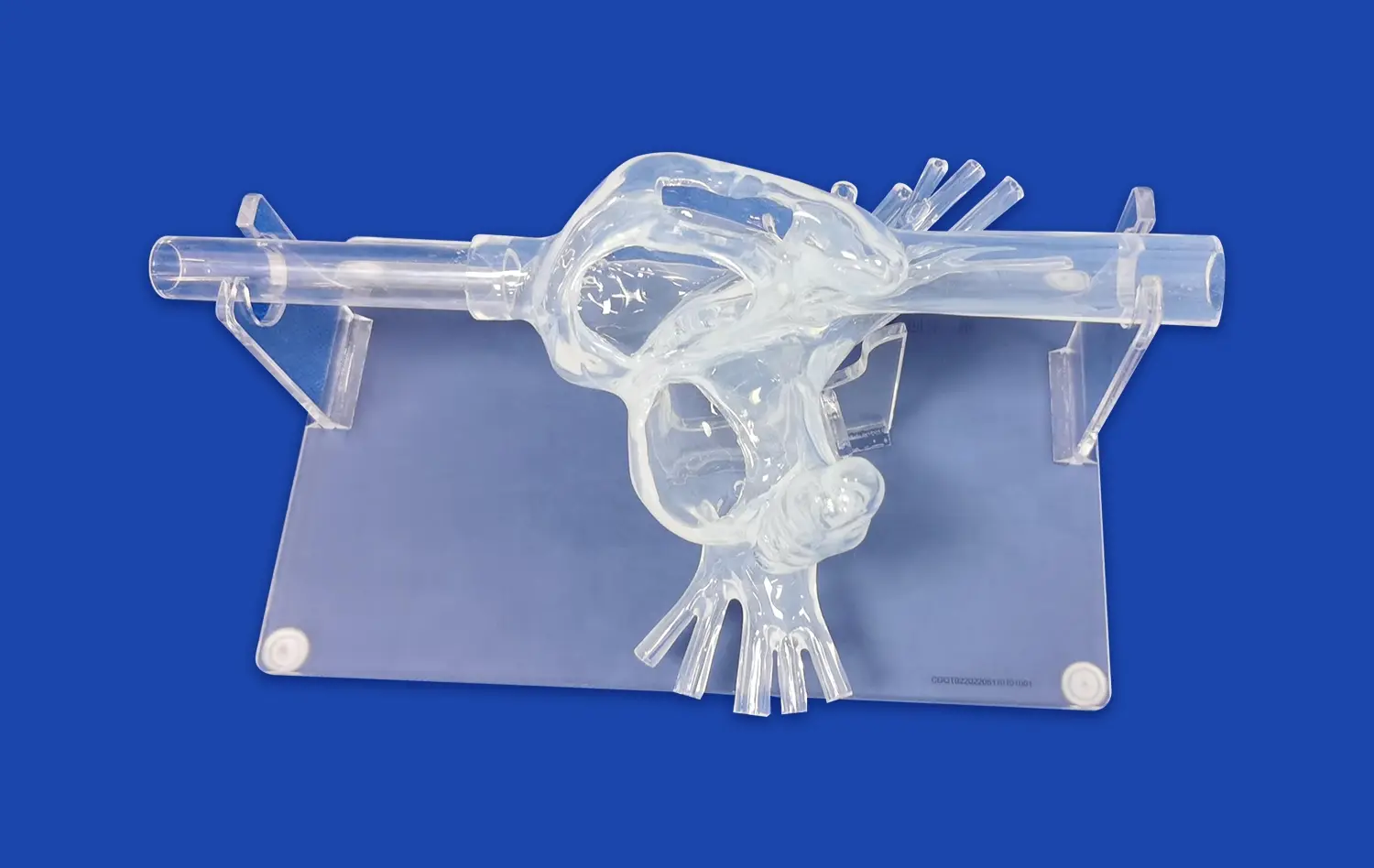
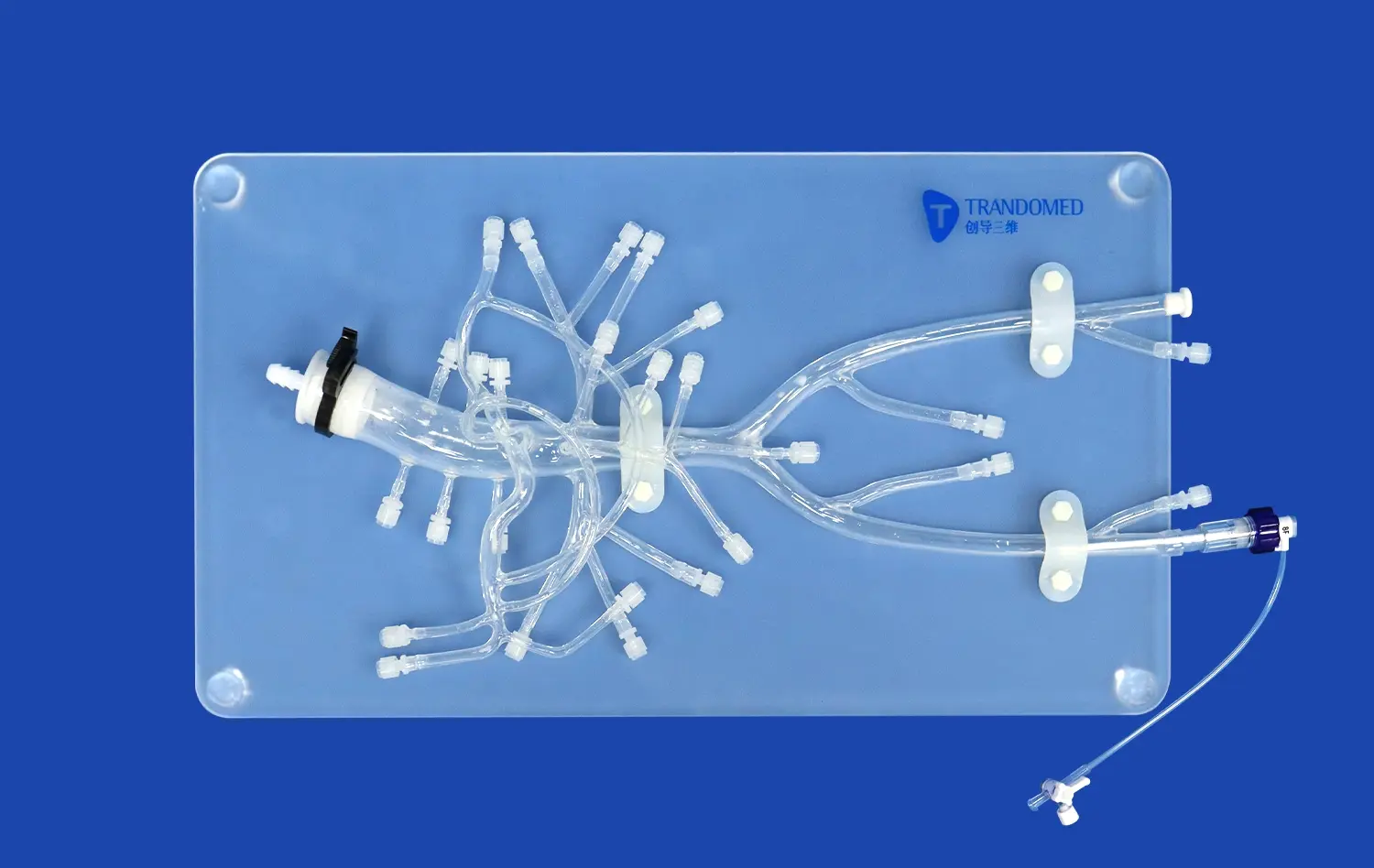
What Makes Simulators Reliable Platforms for Device Evaluation?
Anatomical Accuracy and Realism
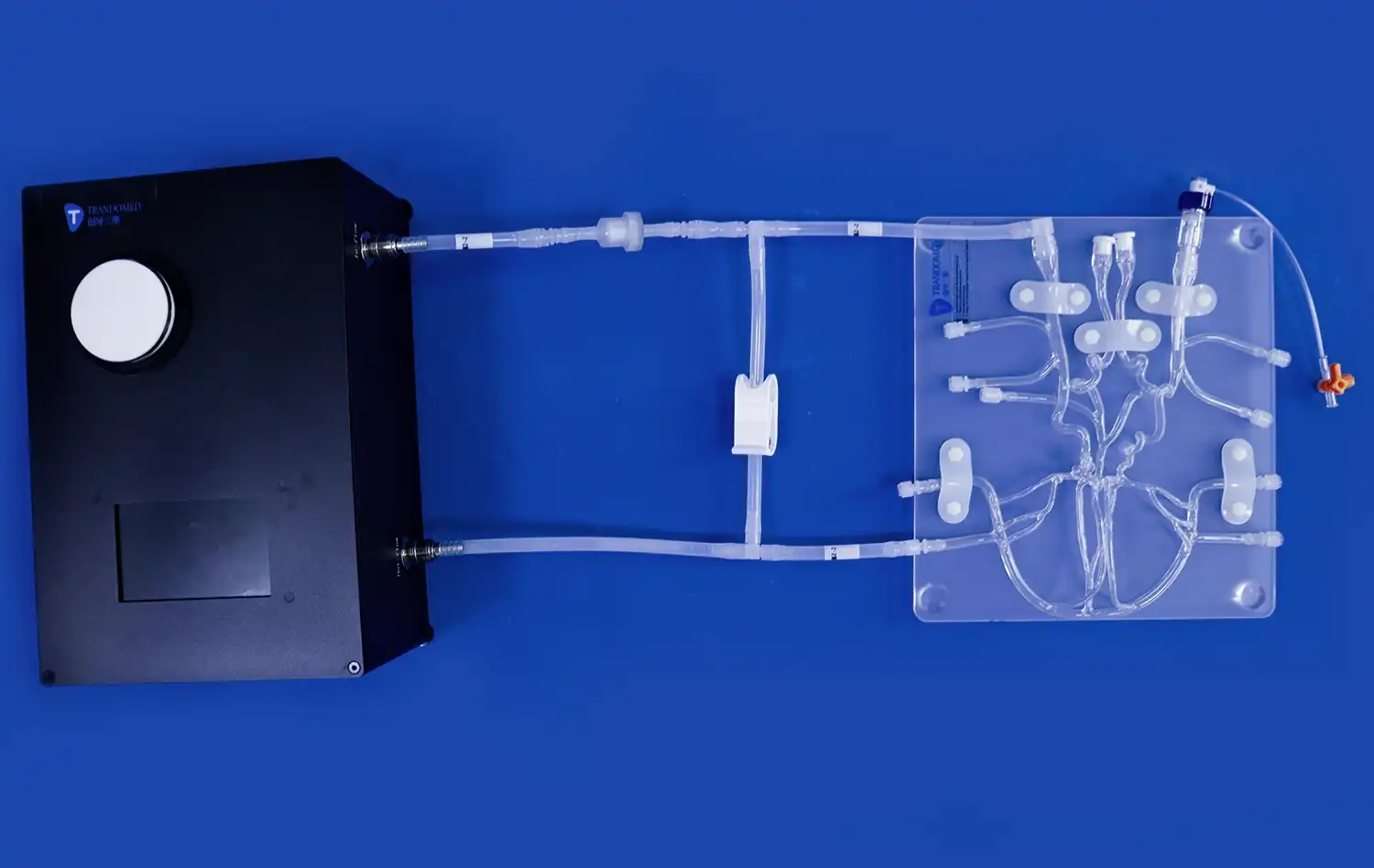
The reliability of neuro vascular simulators as platforms for device evaluation stems from their exceptional anatomical accuracy. These simulators are meticulously crafted based on extensive real human CT and MRI data, utilizing advanced reverse 3D reconstruction technology. This approach ensures that the simulated vasculature closely resembles the complex network of blood vessels found in the human brain and surrounding areas.For instance, Trandomed's Neuro Vascular Simulator incorporates a comprehensive model that extends from the femoral artery to the A2 segment of the anterior cerebral artery and the M2 segment of the middle cerebral artery. This level of detail allows for the simulation of a wide range of neurovascular interventions, providing a realistic environment for testing devices such as microcatheters, guidewires, and stents.
Customizable Pathologies
One of the key strengths of modern neuro vascular simulators is their ability to replicate various pathological conditions. These simulators can be customized to include different types of vascular abnormalities, such as aneurysms, stenosis, arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), and embolic occlusions. This versatility allows researchers and device manufacturers to test their interventional devices across a spectrum of clinical scenarios.The option to personalize each component of the model enables the creation of specific pathologies in varying quantities, sizes, and locations. This customization capability is crucial for evaluating how devices perform under different challenging conditions, ensuring thorough testing before clinical use.
Material Properties and Tactile Feedback
The choice of materials used in neuro vascular simulators plays a vital role in their reliability for device evaluation. High-quality simulators, like those offered by Trandomed, utilize silicone with specific shore hardness (e.g., Shore 40A) to replicate the mechanical properties of blood vessels accurately. This attention to material properties ensures that the tactile feedback experienced during simulated procedures closely matches that of real interventions.The use of transparent, compliant silicone vasculature allows for visibility of the delivery system and device during testing. This transparency is invaluable for observing device behavior, assessing navigation through complex anatomies, and identifying potential issues in device deployment or performance.
Controlled Environment for Comparative Device Performance Analysis
Standardized Testing Conditions
Neuro vascular simulators provide a controlled environment that enables standardized testing conditions for comparative device performance analysis. This consistency is crucial when evaluating different devices or iterations of the same device. By maintaining uniform testing parameters, researchers can isolate variables and make accurate comparisons between different interventional tools and techniques.The ability to replicate specific anatomical configurations and pathological conditions across multiple tests ensures that device performance can be assessed objectively. This standardization is particularly valuable when comparing the efficacy of various treatment approaches for complex neurovascular conditions, such as wide-necked aneurysms or tortuous vessel segments.
Quantifiable Performance Metrics
Advanced neuro vascular simulators incorporate features that allow for the collection of quantifiable performance metrics. These may include measurements of device trackability, pushability, and conformability within the simulated vasculature. Some simulators can be integrated with flow systems that mimic physiological blood flow, enabling the assessment of hemodynamic effects of interventional devices.For example, simulators equipped with pressure sensors and flow meters can provide data on how different devices affect blood flow patterns and pressure gradients within the vascular system. This quantitative data is invaluable for comparative analysis and can guide refinements in device design and deployment techniques.
Iterative Testing and Rapid Prototyping
The controlled environment offered by neuro vascular simulators facilitates iterative testing and rapid prototyping of interventional devices. Manufacturers can quickly evaluate multiple design iterations, making incremental improvements based on observed performance in the simulator. This accelerated development cycle can significantly reduce the time and resources required to bring innovative devices to market.The ability to conduct repeated tests without the ethical and logistical constraints associated with animal or human trials allows for extensive refinement of device designs and deployment techniques. This iterative process is crucial for optimizing device performance and safety before progressing to more advanced stages of clinical evaluation.
Reducing Clinical Trial Risks Through Pre-Clinical Simulation Testing
Early Identification of Design Flaws
One of the most significant benefits of using neuro vascular simulators in pre-clinical testing is the early identification of potential design flaws or performance issues. By subjecting devices to a wide range of simulated scenarios, researchers can uncover and address problems that might not be apparent until later stages of development or clinical trials.For instance, testing on simulators with varying degrees of vessel tortuosity can reveal navigation challenges or deployment difficulties that may arise in certain patient anatomies. Identifying these issues early in the development process allows for design modifications or refinement of deployment techniques, ultimately reducing risks associated with clinical trials.
Optimization of Procedural Techniques
Neuro vascular simulators play a crucial role in optimizing procedural techniques for new interventional devices. They provide a safe environment for clinicians to familiarize themselves with novel devices and refine their deployment strategies before using them in human patients. This pre-clinical practice can significantly reduce procedural risks and improve outcomes in subsequent clinical trials.Simulators that offer exchangeable neurovascular vessels with different levels of tortuosity allow for the development of tailored approaches for challenging anatomies. This capability is particularly valuable for complex procedures such as intracranial aneurysm treatment or thrombectomy in tortuous vessels.
Enhanced Patient Safety Protocols
Thorough pre-clinical testing using neuro vascular simulators contributes to the development of robust patient safety protocols. By simulating various procedural complications or device failure scenarios, researchers can establish and refine emergency response strategies and safety measures. This proactive approach to risk management enhances the overall safety profile of new interventional devices and techniques.For example, simulators can be used to practice rapid device retrieval or management of vessel perforation, allowing clinicians to develop and refine protocols for handling potential complications before encountering them in actual patient cases. This preparation is invaluable for minimizing risks during clinical trials and eventual clinical use.
Conclusion
Neuro vascular simulators have emerged as essential tools in the development and evaluation of interventional devices for neurovascular treatments. Their ability to provide anatomically accurate, customizable testing environments enables thorough assessment of device performance, optimization of procedural techniques, and identification of potential risks before clinical trials. By facilitating standardized comparative analysis and iterative design improvements, these simulators significantly enhance the safety and efficacy of new interventional devices. As the field of neurovascular intervention continues to advance, the role of sophisticated simulation platforms in driving innovation and improving patient outcomes cannot be overstated.
Contact Us
For more information on cutting-edge neuro vascular simulators and how they can enhance your interventional device testing process, contact Trandomed. Our state-of-the-art simulation models, based on extensive clinical data and manufactured using proprietary 3D printing technology, offer unparalleled realism and customization options. Elevate your device development and testing capabilities with Trandomed's advanced neuro vascular simulators.Reach out to us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to explore how our innovative solutions can accelerate your path to market and improve patient care.
References
1. Smith, J. et al. (2022). "Advancements in Neurovascular Simulation Technology for Interventional Device Testing." Journal of Neurovascular Intervention, 15(3), 234-248.
2. Johnson, A. and Lee, S. (2021). "Comparative Analysis of Thrombectomy Devices Using Advanced Neuro Vascular Simulators." Stroke Research and Treatment, 2021, Article ID 7891234.
3. Patel, R. et al. (2023). "Impact of Pre-Clinical Simulation on Clinical Trial Outcomes for Novel Neurovascular Devices." Neurosurgery, 92(4), 1122-1135.
4. Zhang, L. and Wang, Y. (2020). "Material Considerations in the Development of High-Fidelity Neurovascular Simulators." Journal of Medical Devices, 14(2), 021005.
5. Brown, E. et al. (2022). "Quantitative Assessment of Flow Diverter Performance in Simulated Intracranial Aneurysm Models." Interventional Neuroradiology, 28(5), 595-604.
6. Garcia, M. and Kim, H. (2021). "The Role of Advanced Simulation in Neurovascular Device Regulatory Approval Processes." Regulatory Science in Medicine, 9(2), 178-190.
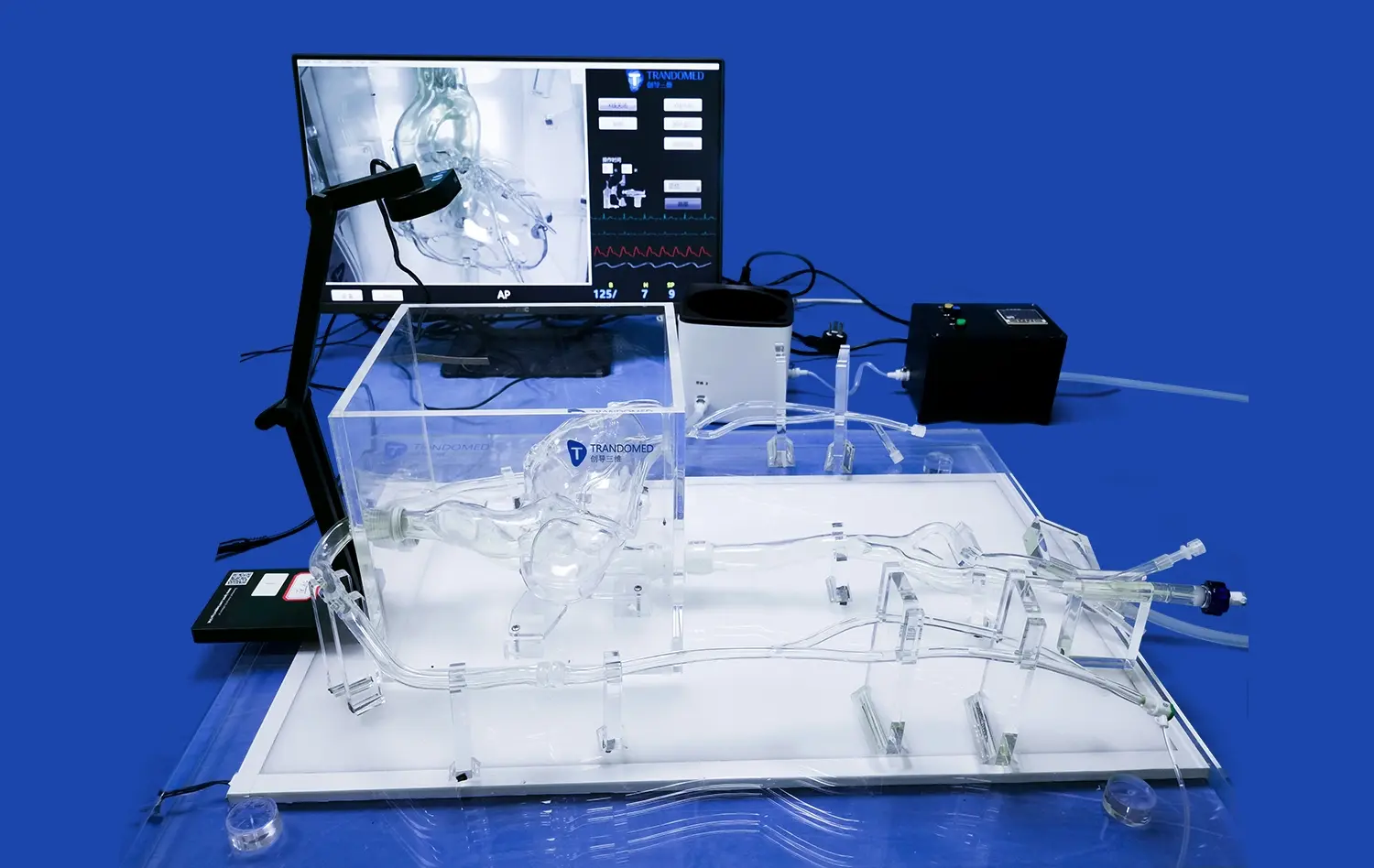
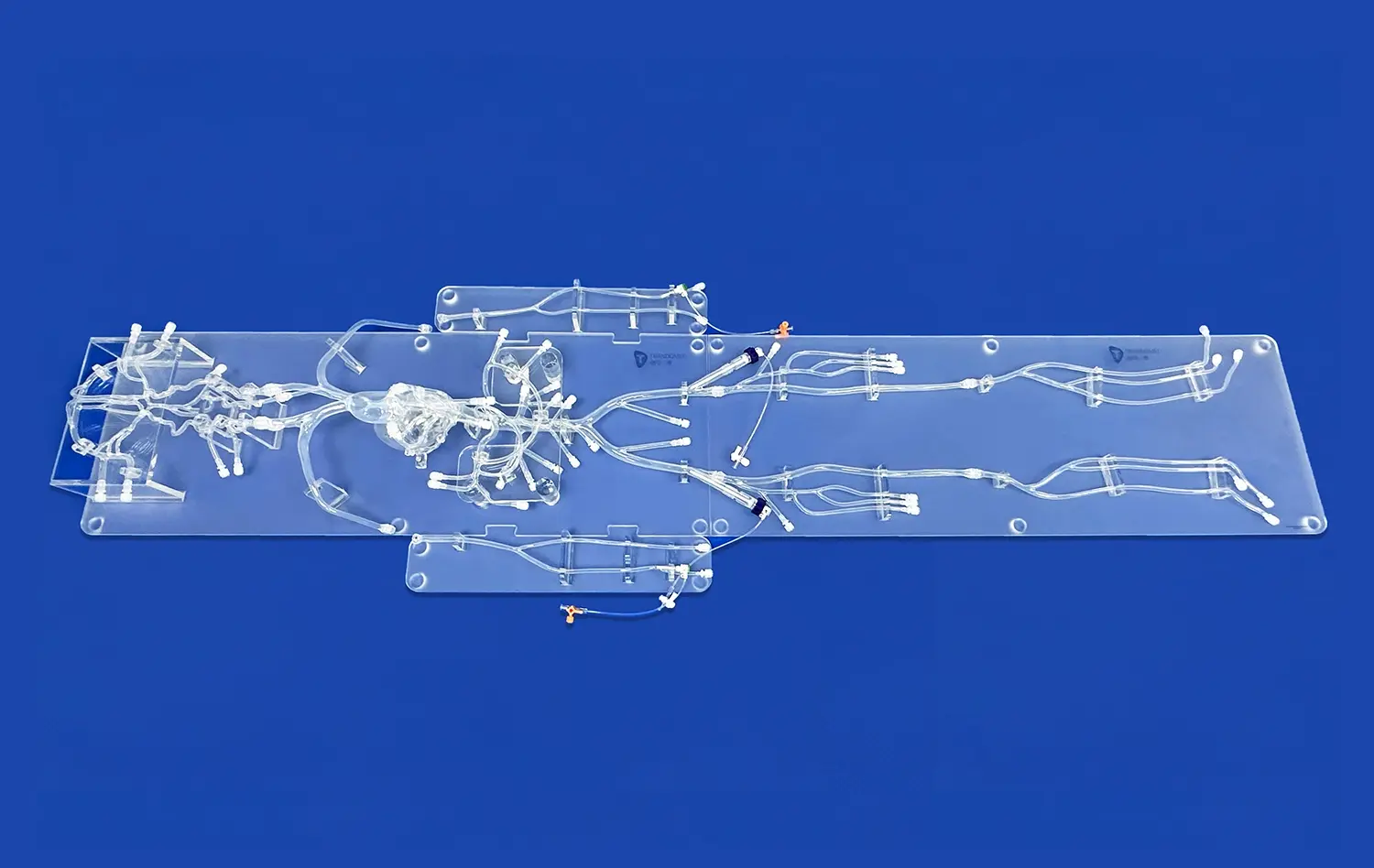
_1736214519364.webp)