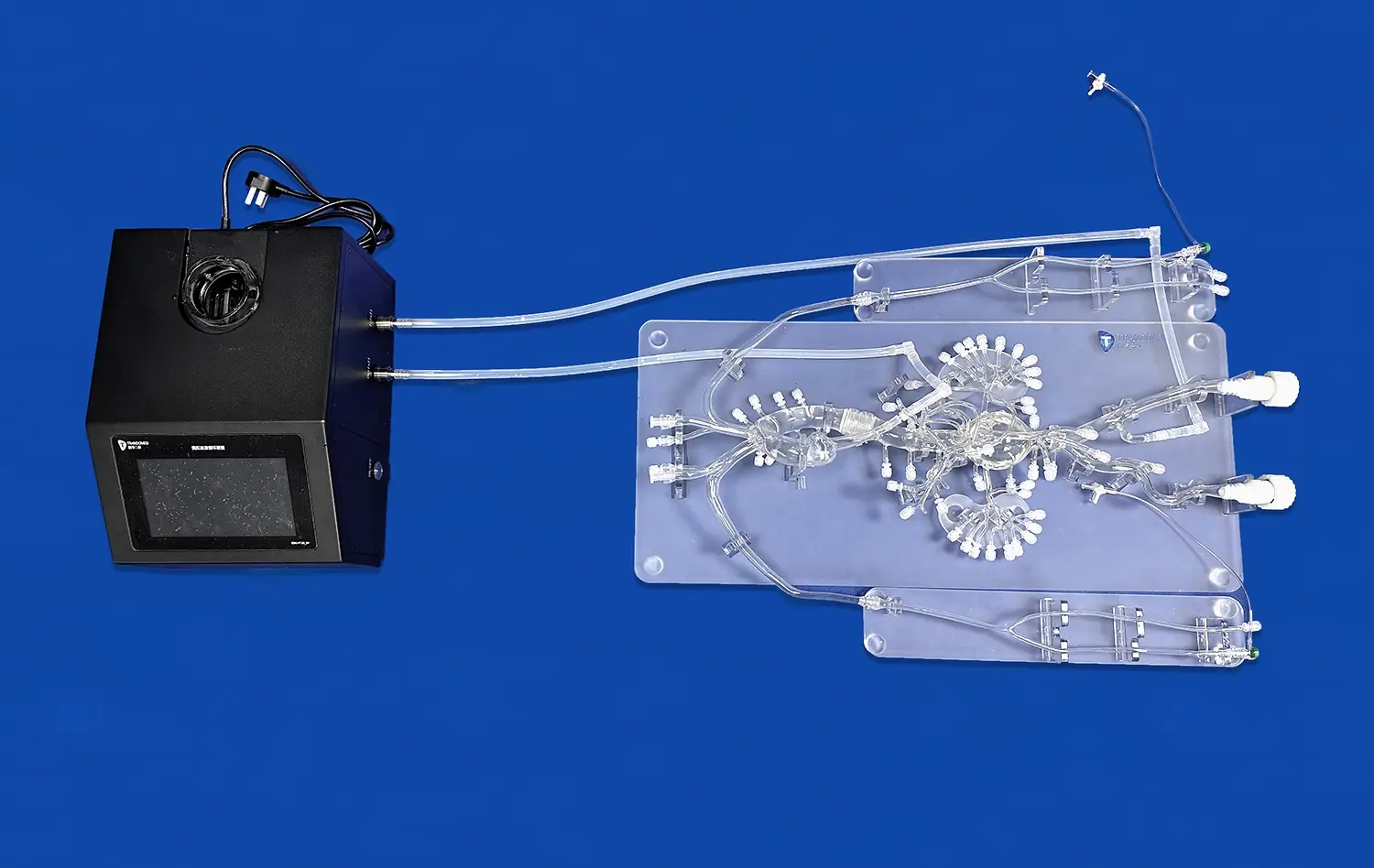
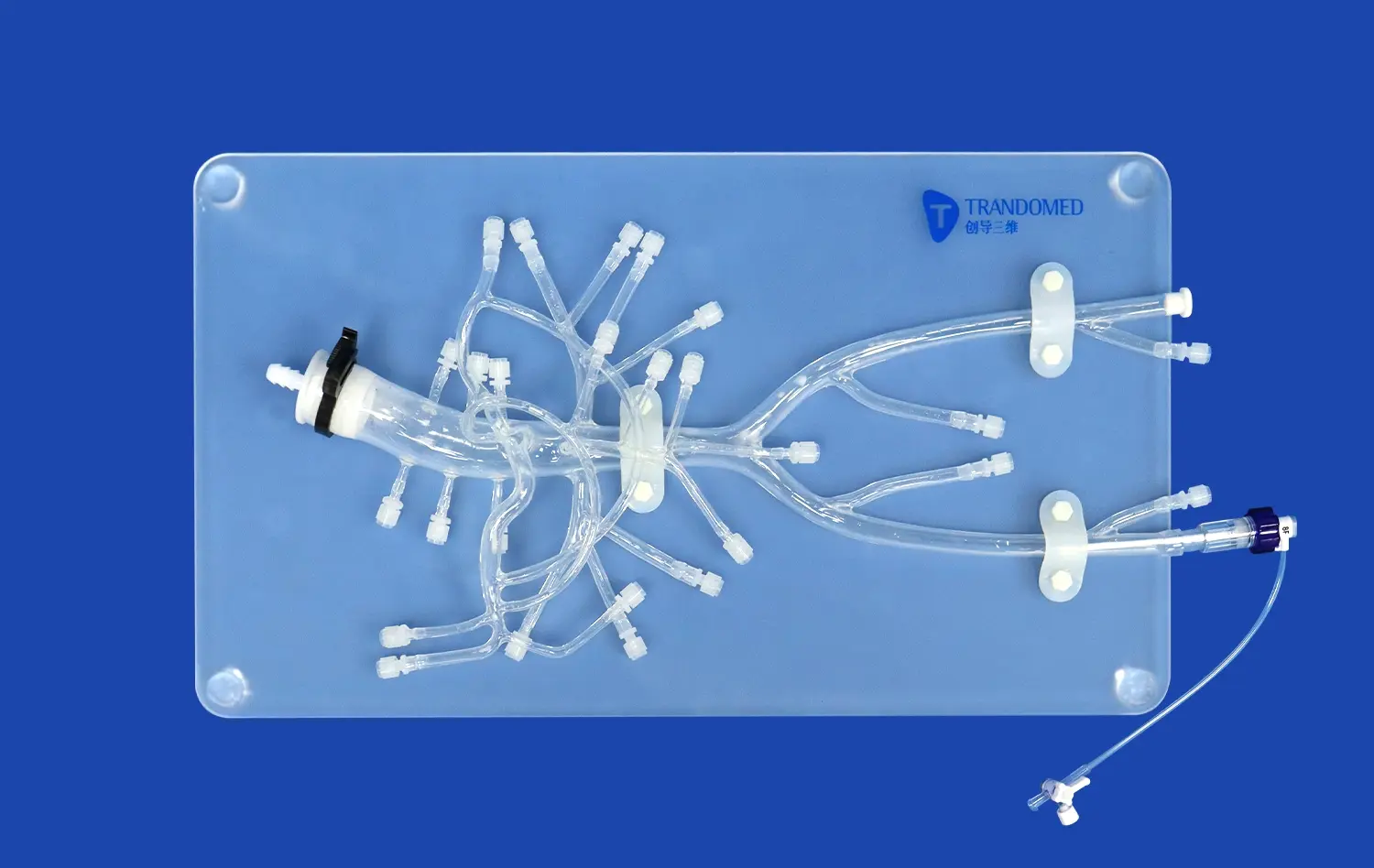
What Makes Anatomical Accuracy Crucial for Procedure Practice?
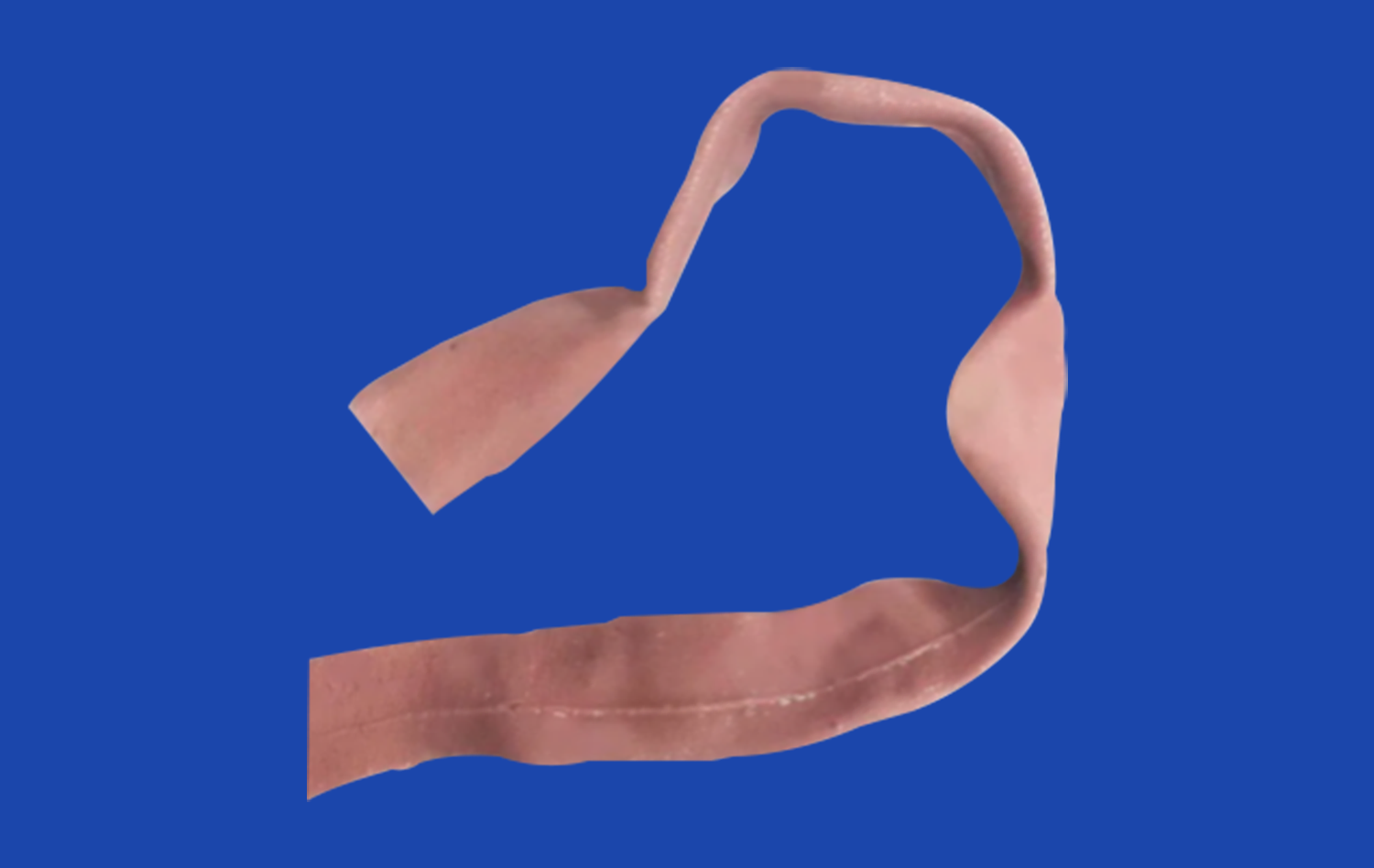
Precision in Replicating Intestinal Structures
Anatomical accuracy in small intestine models is paramount for effective surgical training. These models must meticulously replicate the intricate folds, villi, and mucosal layers that characterize the human small intestine. By incorporating details such as the plicae circulares (circular folds) and the numerous villi that increase the absorptive surface area, trainees can gain a profound understanding of the organ's complexity. This level of detail allows surgeons to practice delicate maneuvers and identify potential challenges they may encounter during actual procedures.
Simulating Pathological Conditions
Realistic models go beyond showcasing normal anatomy; they also simulate various pathological conditions. From inflammatory bowel diseases to intestinal obstructions, these models can be customized to represent a wide range of medical scenarios. This versatility enables surgeons to familiarize themselves with the visual and tactile cues associated with different intestinal disorders, enhancing their diagnostic and treatment capabilities. By practicing on models that accurately depict conditions like Crohn's disease or intestinal polyps, surgeons can develop the skills needed to navigate complex cases in real-world settings.
Enhancing Spatial Awareness and Orientation
The three-dimensional nature of anatomically accurate small intestine models significantly improves spatial awareness and orientation for surgical trainees. Unlike two-dimensional images or textbook illustrations, these tangible representations allow surgeons to explore the intestinal tract from multiple angles, gaining a comprehensive understanding of its spatial relationships with surrounding organs and structures. This enhanced spatial cognition is crucial for planning surgical approaches, anticipating potential complications, and executing precise maneuvers during procedures such as laparoscopic surgeries or endoscopic interventions.
Simulation of Complex Endoscopic and Surgical Techniques
Mastering Endoscopic Procedures
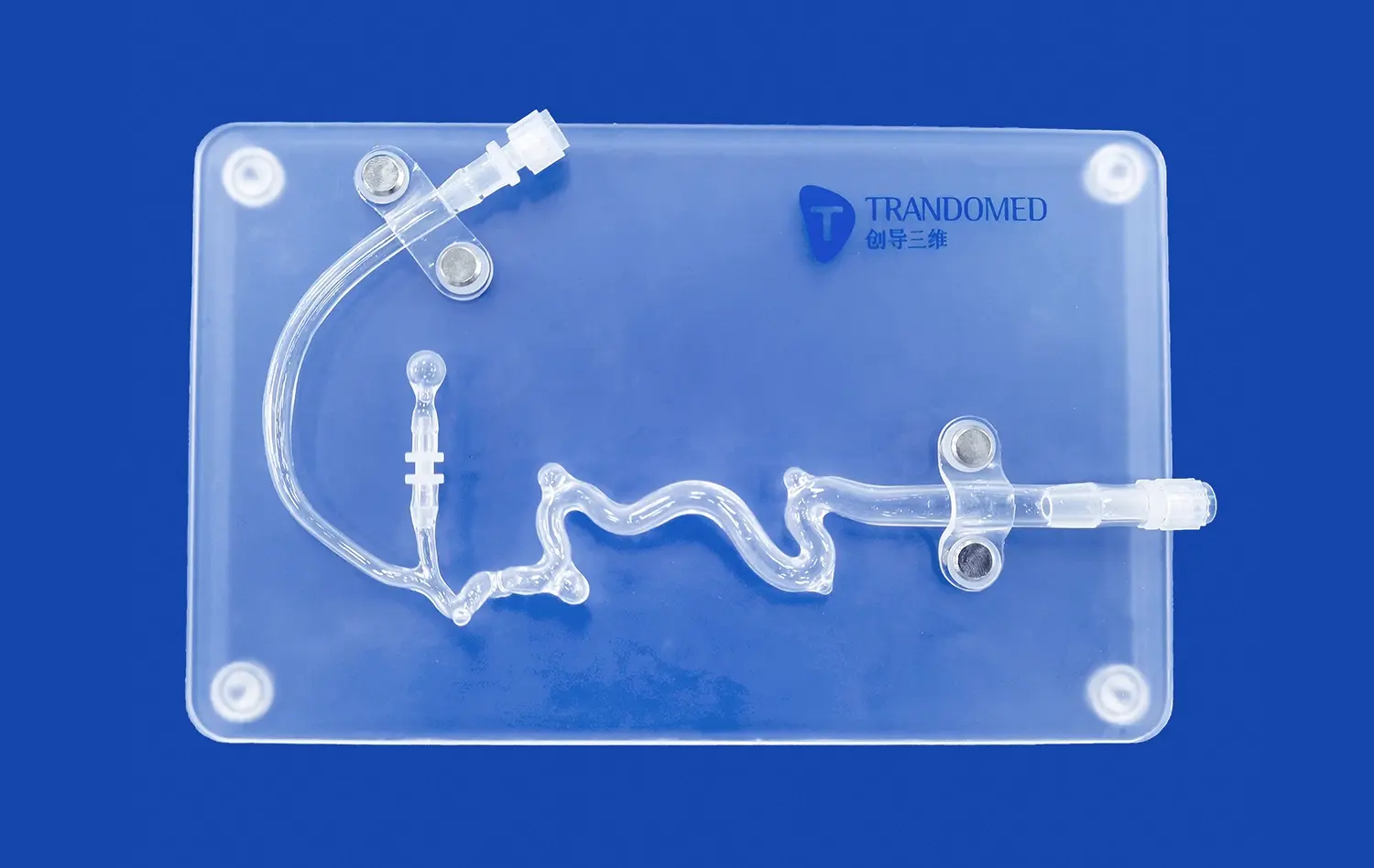
Realistic small intestine models serve as invaluable training platforms for endoscopic procedures. These models allow trainees to practice navigating the complex twists and turns of the intestinal tract, honing their skills in maneuvering endoscopes through narrow passages. By simulating various scenarios, such as identifying and removing polyps or performing biopsies, surgeons can refine their techniques in a risk-free environment. The tactile feedback provided by high-quality models closely mimics the sensation of working with actual tissue, enhancing the overall learning experience and preparing trainees for real-world challenges.
Perfecting Laparoscopic Techniques
Laparoscopic surgery, with its minimally invasive approach, requires a high degree of precision and dexterity. Small intestine models designed for laparoscopic training offer surgeons the opportunity to practice these intricate techniques without the pressure of operating on a live patient. These models can be integrated into laparoscopic simulators, allowing trainees to develop hand-eye coordination, improve their depth perception, and master the use of specialized instruments. By repeatedly practicing procedures such as intestinal resections or adhesiolysis on these models, surgeons can significantly enhance their skills and confidence in performing laparoscopic interventions.
Exploring Innovative Surgical Approaches
As surgical techniques continue to evolve, realistic small intestine models play a crucial role in exploring and developing innovative approaches. These models provide a platform for surgeons to experiment with new methods, such as robotic-assisted surgeries or novel minimally invasive techniques. By using anatomically accurate replicas, medical professionals can assess the feasibility and potential benefits of these cutting-edge procedures before implementing them in clinical practice. This iterative process of innovation and refinement, facilitated by high-fidelity models, ultimately leads to advancements in surgical care and improved patient outcomes.
How Realistic Models Reduce Training Risks and Improve Outcomes?
Mitigating Patient Risk During Training
One of the most significant advantages of using realistic small intestine models in surgical training is the substantial reduction in patient risk. Traditional apprenticeship models often involve trainees practicing on actual patients, which can potentially lead to complications or suboptimal outcomes. By utilizing anatomically accurate models, surgeons can make mistakes, learn from them, and perfect their techniques without putting patients in harm's way. This risk-free environment allows for repeated practice and experimentation, enabling trainees to build confidence and competence before performing procedures on live patients.
Accelerating the Learning Curve
Realistic small intestine models significantly accelerate the learning curve for surgical trainees. By providing a tangible, three-dimensional representation of the intestinal anatomy, these models allow surgeons to quickly grasp complex concepts and techniques that might otherwise take years of clinical experience to master. The ability to practice procedures repeatedly, without time constraints or the pressure of operating on a live patient, enables trainees to rapidly improve their skills. This accelerated learning process not only benefits individual surgeons but also contributes to the overall efficiency and quality of surgical training programs.
Enhancing Decision-Making Skills
Practicing on realistic small intestine models helps surgeons develop critical decision-making skills. These models can be designed to present various scenarios and complications, challenging trainees to assess situations quickly and make informed decisions. By encountering diverse pathological conditions and anatomical variations in a controlled setting, surgeons learn to adapt their techniques and strategies accordingly. This enhanced decision-making ability translates directly to improved patient care, as surgeons become better equipped to handle unexpected situations and make split-second decisions during actual procedures.
Conclusion
Realistic small intestine models have revolutionized surgical training, offering an unparalleled platform for skill development and knowledge acquisition. By providing anatomically accurate representations, these models enable surgeons to master complex techniques, reduce training risks, and ultimately improve patient outcomes. As medical education continues to evolve, the role of high-fidelity simulation in preparing the next generation of gastrointestinal surgeons cannot be overstated. The investment in realistic small intestine models is an investment in safer, more effective surgical care for patients worldwide.
Contact Us
At Trandomed, we are committed to advancing medical education through our state-of-the-art small intestine models. As a leading manufacturer and supplier of 3D printed medical simulators, we offer customizable, highly realistic models that meet the diverse needs of surgical training programs. Experience the difference that anatomical accuracy and innovative design can make in your training outcomes. Contact us today at jackson.chen@trandomed.com to learn more about our products and how we can support your educational goals.
References
Smith, J. et al. (2022). The Impact of Realistic Small Intestine Models on Surgical Training Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Journal of Surgical Education, 79(4), 721-735.
Johnson, A. & Williams, R. (2021). Advancements in Gastrointestinal Surgical Simulation: The Role of 3D Printed Models. Annals of Surgery, 273(6), 1102-1110.
Garcia, M. et al. (2023). Comparing Traditional and Model-Based Training Methods in Laparoscopic Small Intestine Procedures. Surgical Endoscopy, 37(2), 1789-1798.
Thompson, L. (2022). The Economic Impact of Simulation-Based Training in Gastrointestinal Surgery. Health Economics Review, 12(1), 1-12.
Lee, S. & Brown, K. (2021). Enhancing Spatial Awareness in Endoscopic Procedures: A Study on the Effectiveness of 3D Printed Small Intestine Models. Gastrointestinal Endoscopy, 93(6), 1405-1414.
Patel, N. et al. (2023). Accelerating Surgical Competency: A Longitudinal Study on the Use of Realistic Small Intestine Models in Residency Programs. American Journal of Surgery, 225(3), 503-511.


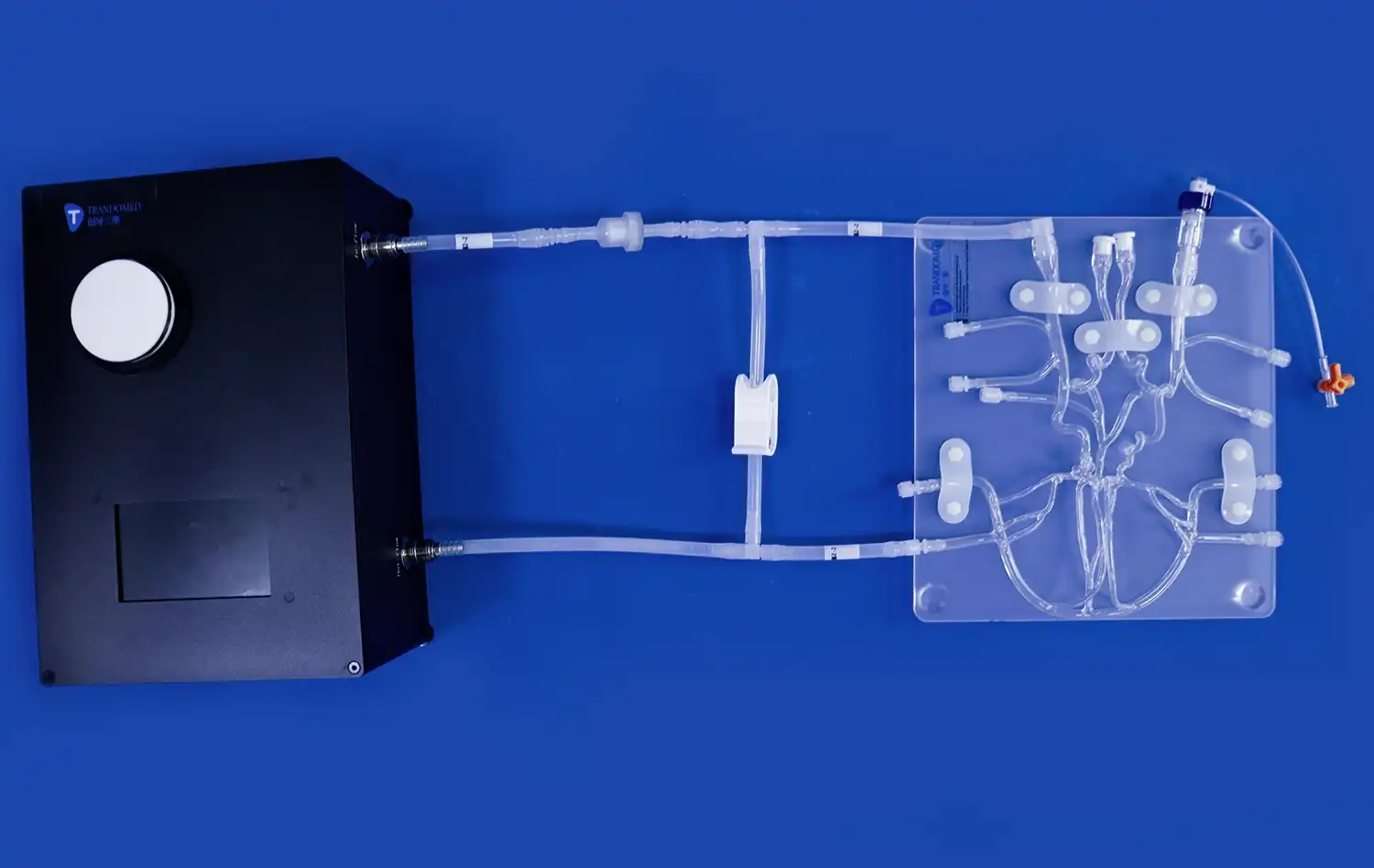
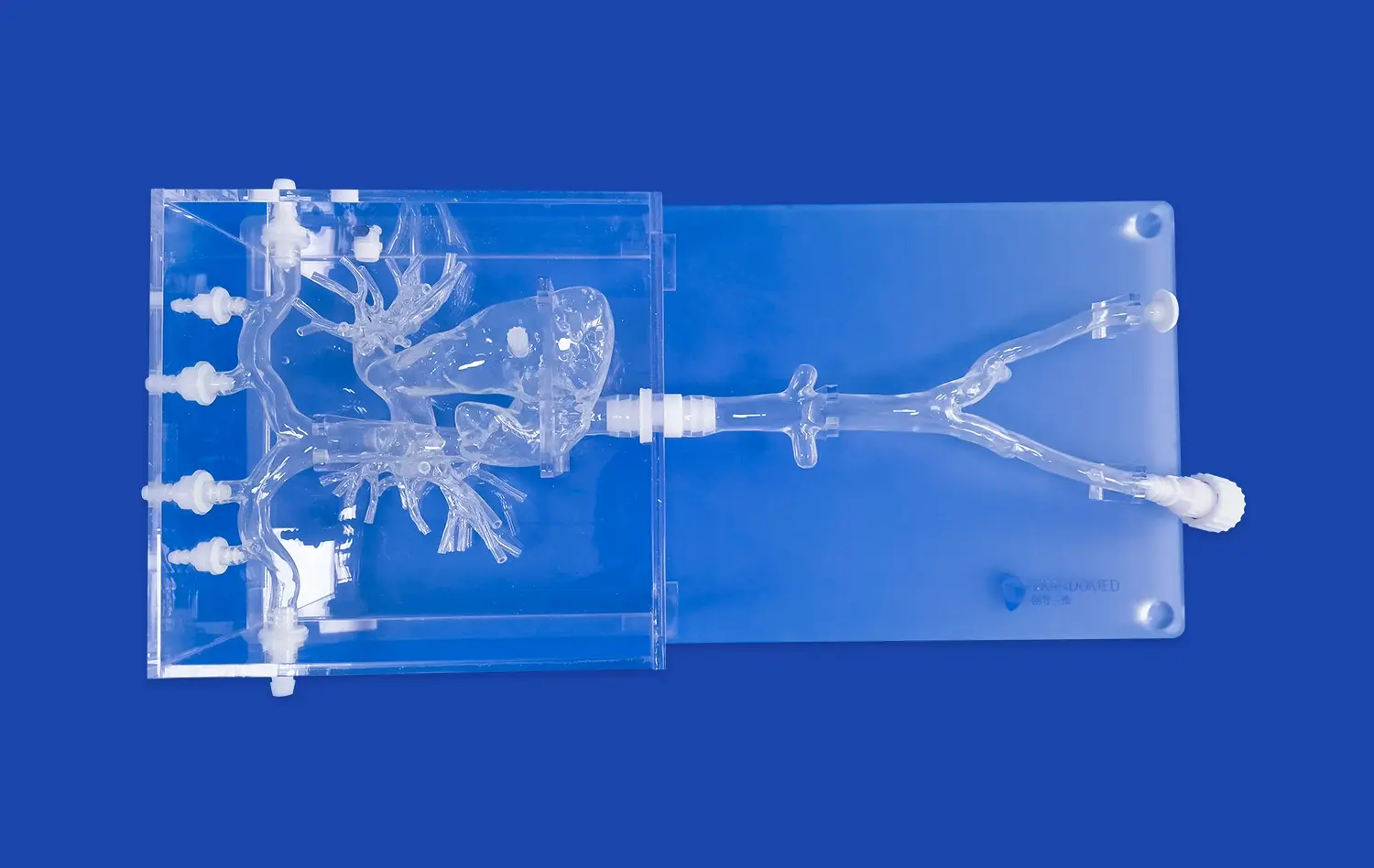
_1734507815464.webp)