What Makes It Indispensable in Gastroenterology Curriculum?
Unparalleled Realism in Anatomical Representation
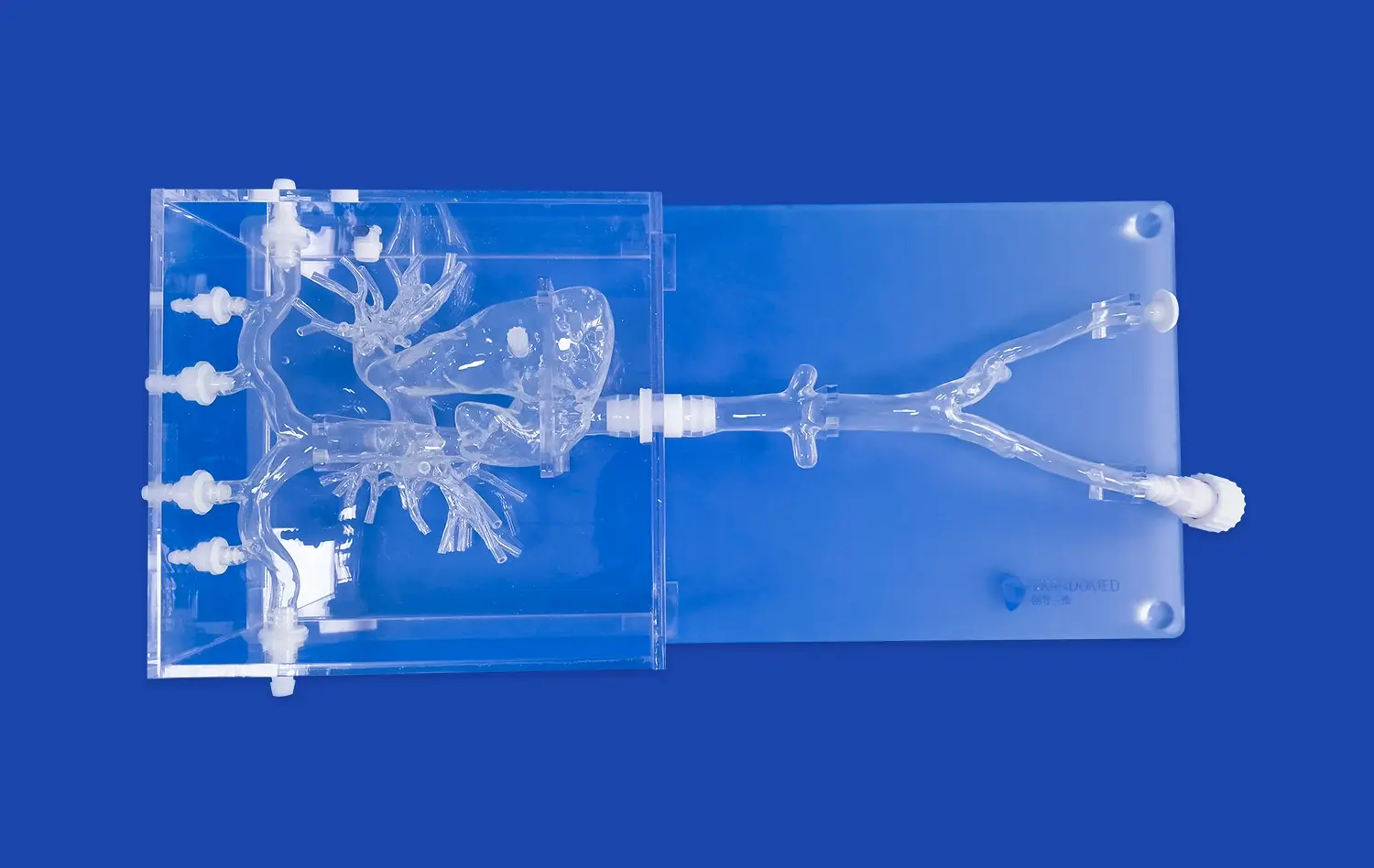
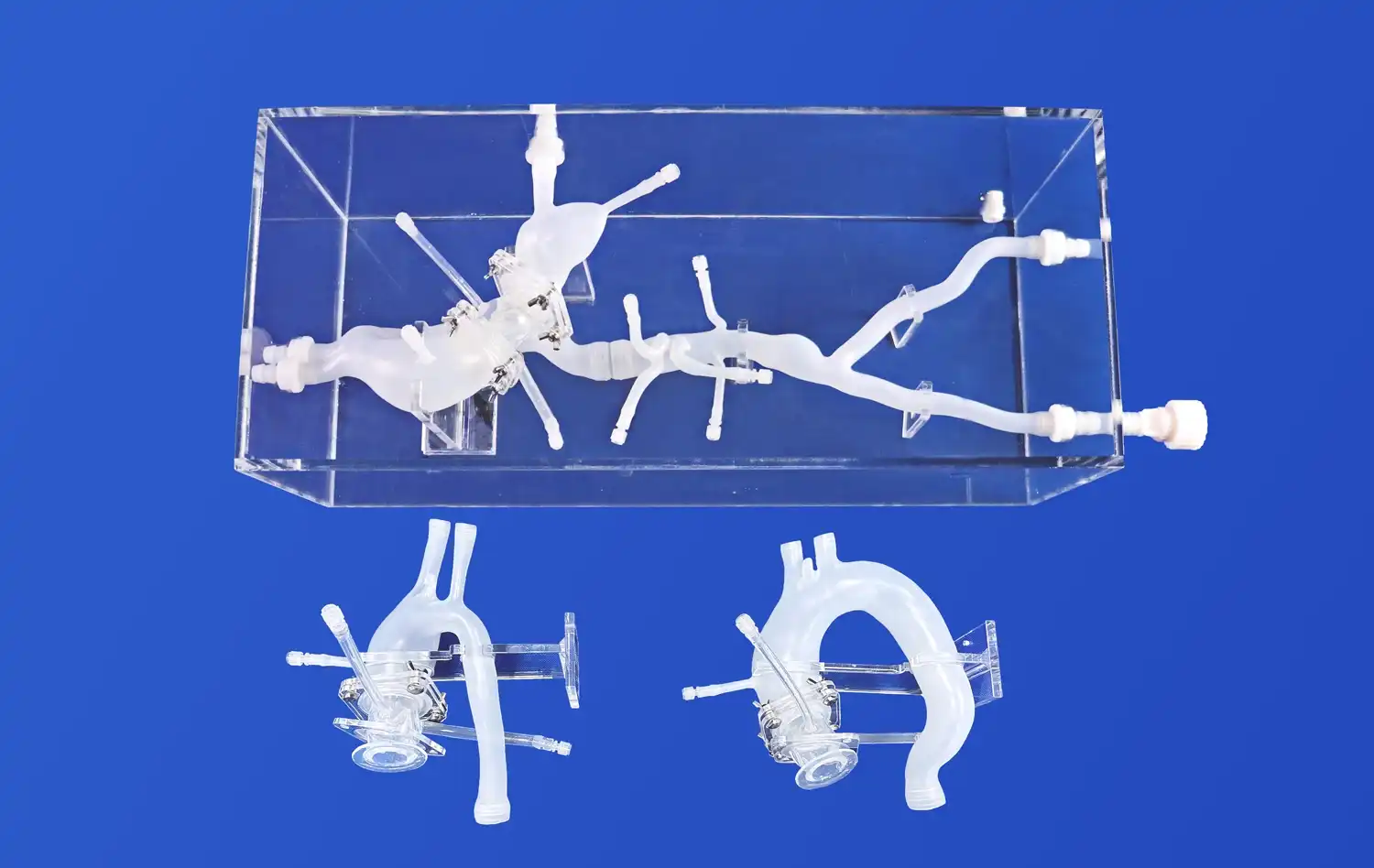
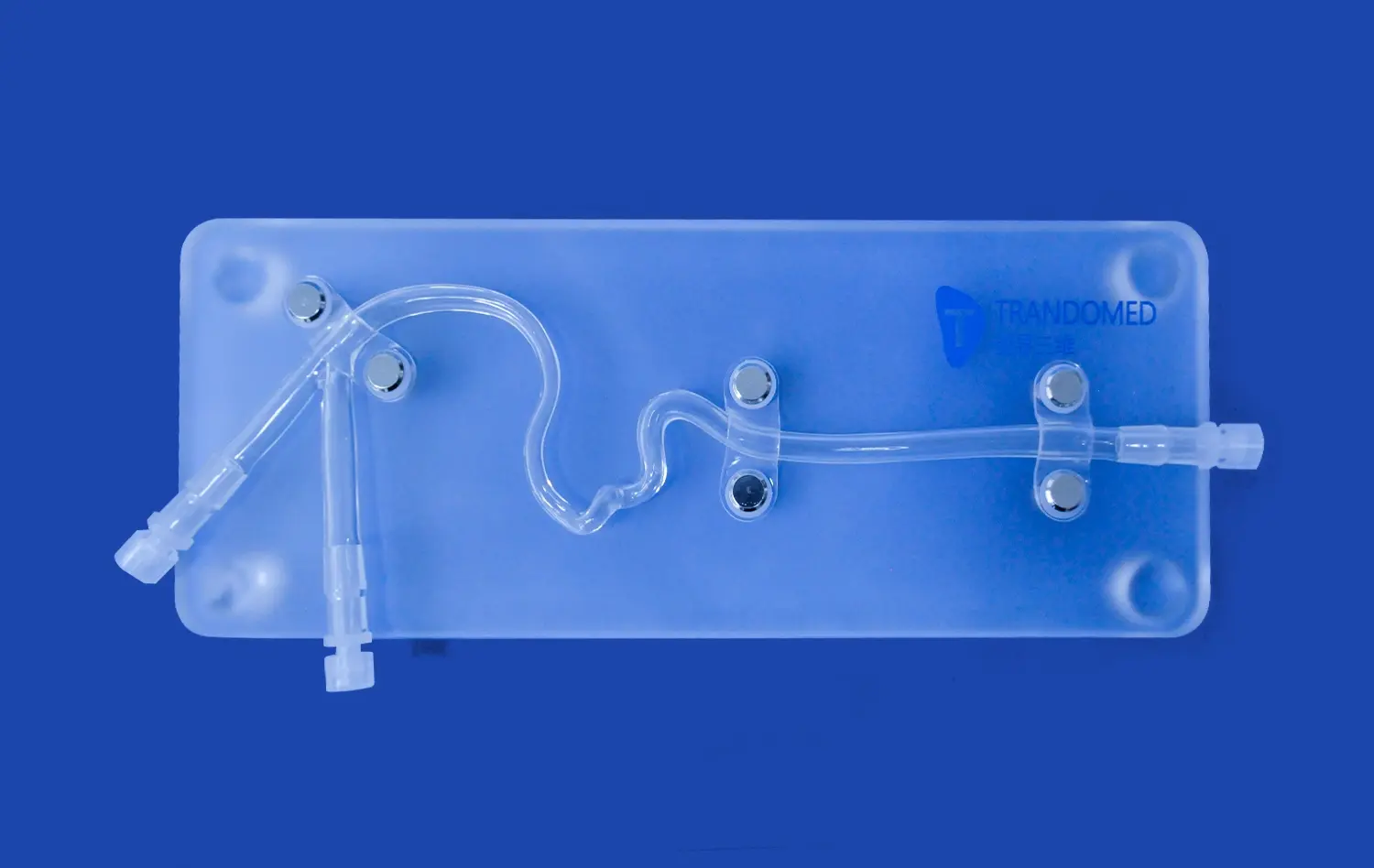
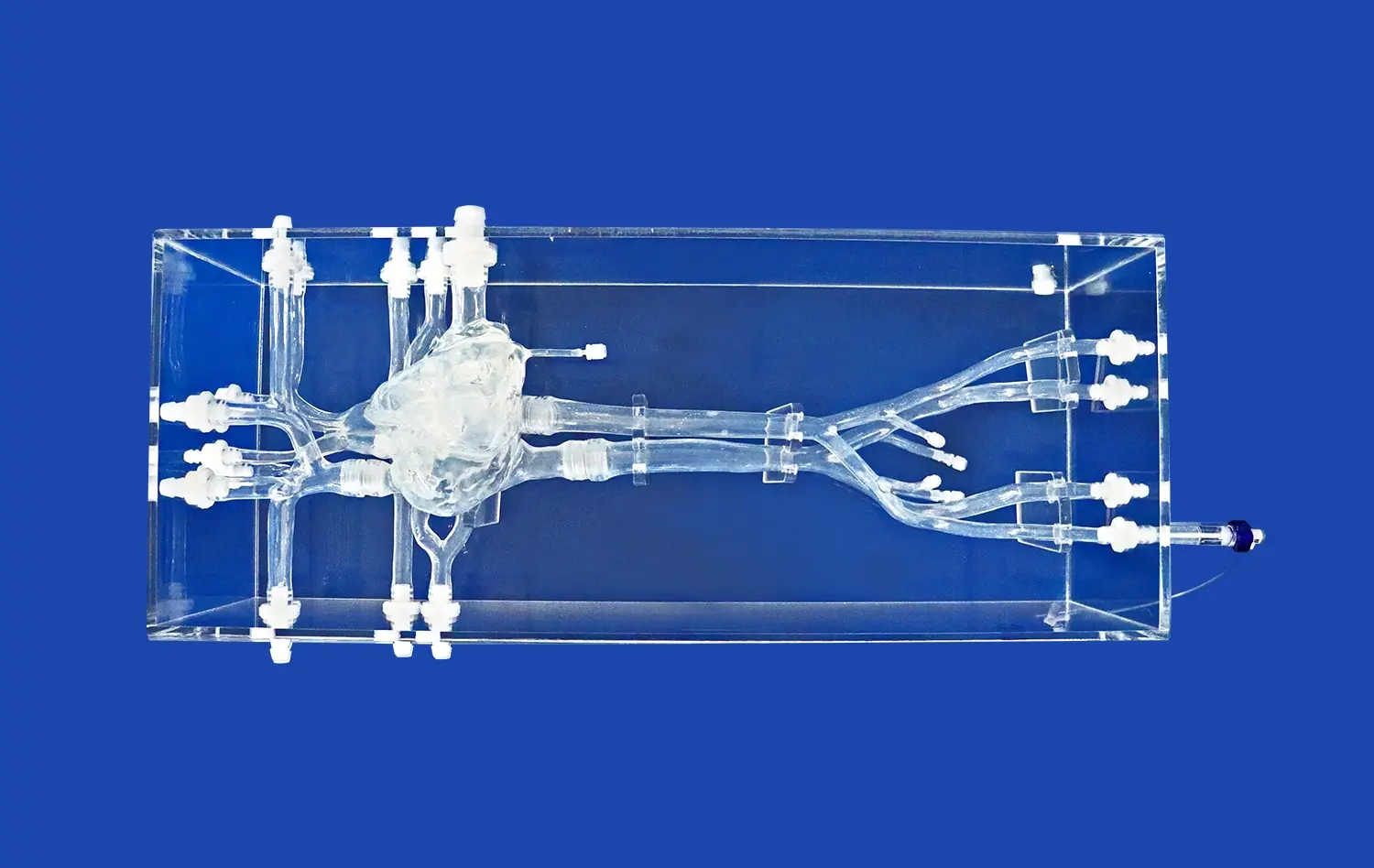
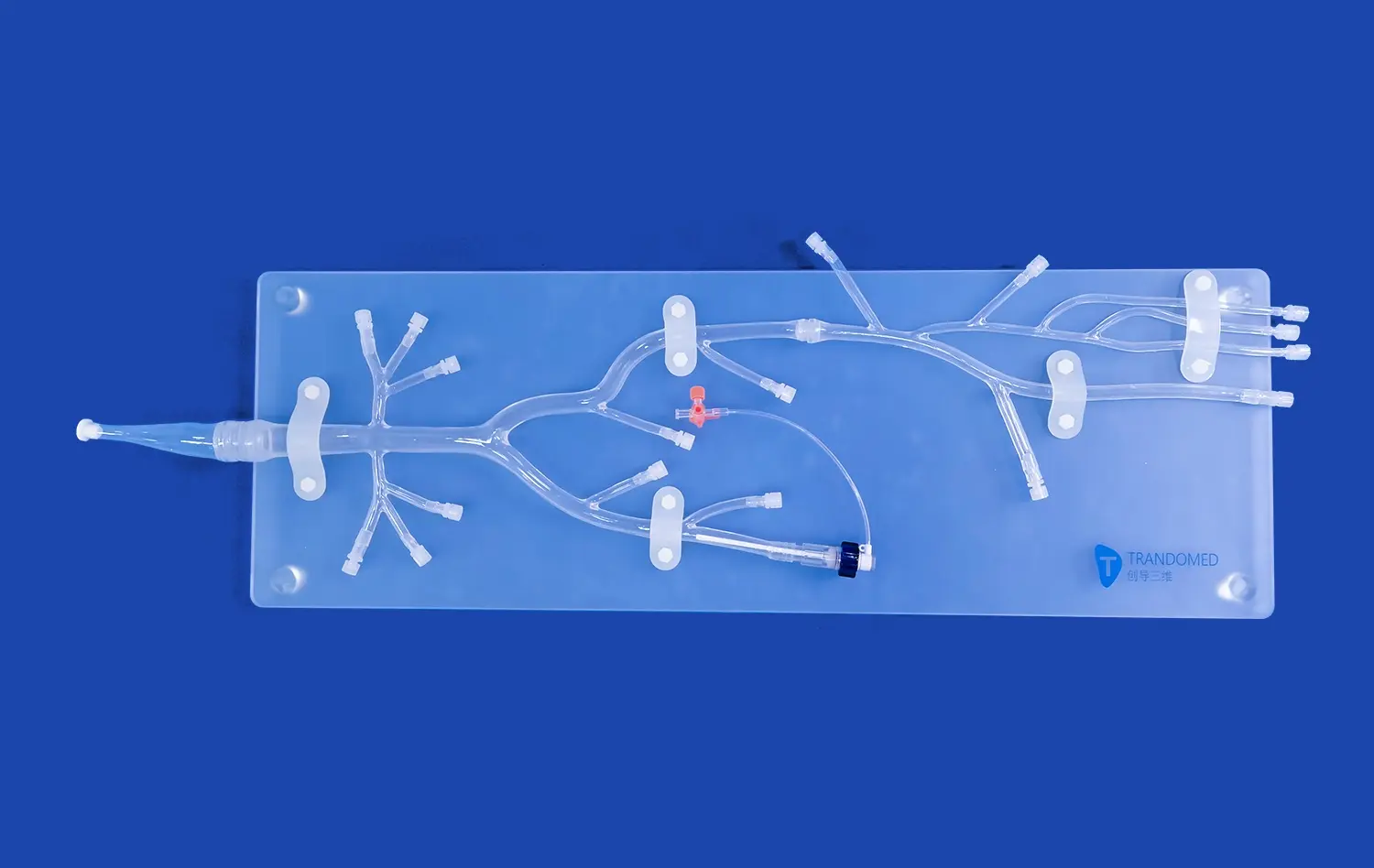
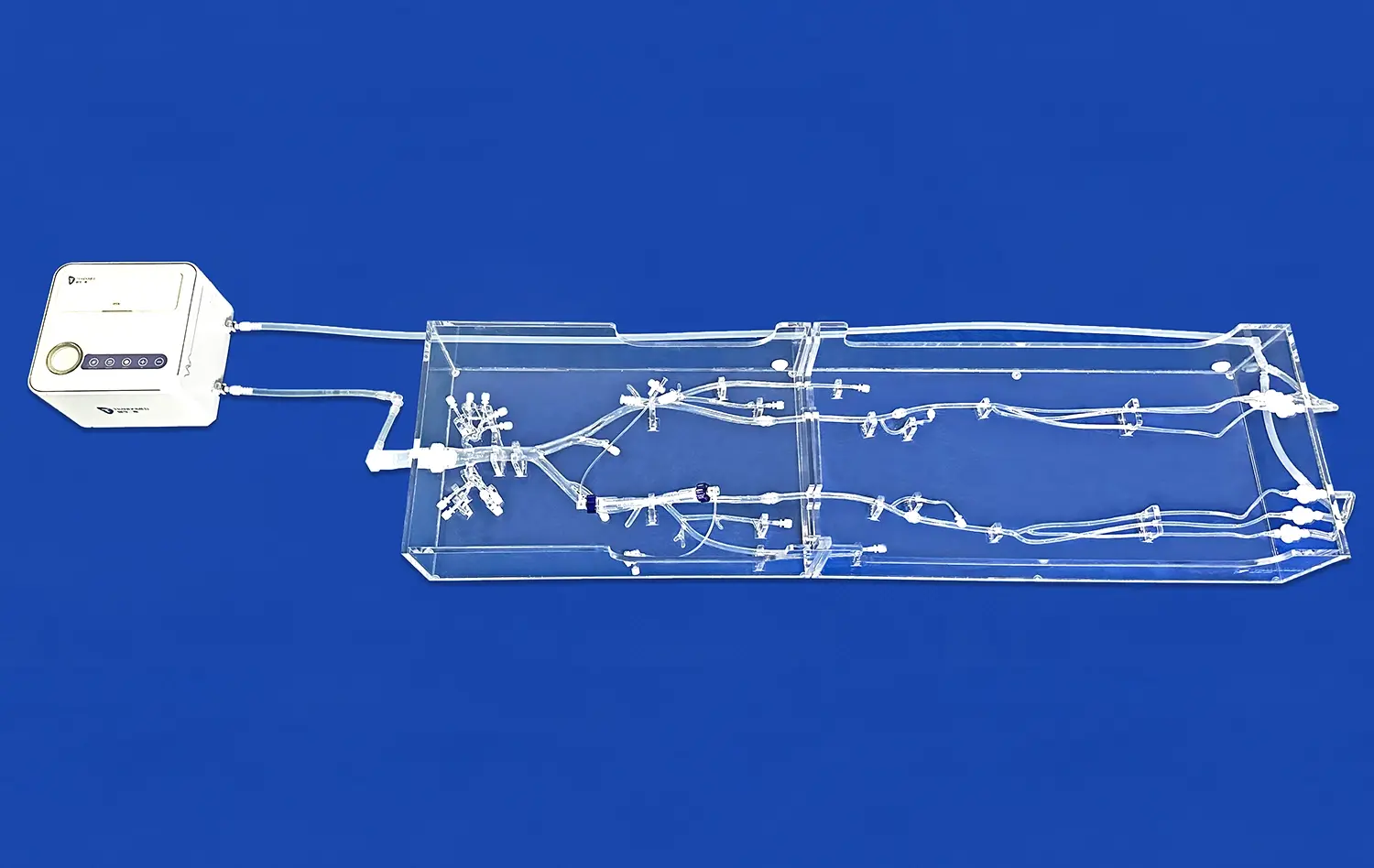
The ERCP Simulator II stands out for its exceptional anatomical accuracy. Crafted using advanced 3D printing technology and based on real human CT and MRI data, this simulator offers an unparalleled representation of the human digestive system. It includes meticulously designed components such as the esophagus, cardiac region, stomach, pylorus, duodenum, common bile duct, cystic duct, gallbladder, hepatic duct, and left and right hepatic ducts. The use of soft silicone material with a Shore 40A hardness replicates the texture and feel of human tissue, providing trainees with a tactile experience that closely mimics real-life procedures.
Versatility in Training Scenarios
One of the key strengths of the ERCP Simulator II is its versatility. It caters to a wide array of training needs within the gastroenterology field. From basic endoscopy training to advanced ERCP operations, this simulator serves as a comprehensive platform for skill development. Trainees can practice upper gastrointestinal endoscopy, including procedures involving the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum. The simulator also excels in ERCP-specific training, allowing learners to simulate the removal of calculi from various ducts and the gallbladder. Furthermore, its customizable features enable the addition of pathological elements like gastric ulcers, early-stage gastric cancer, and polyps, enhancing diagnostic and treatment training capabilities.
Continuous Skill Refinement and Assessment
The ERCP Simulator II plays a crucial role in continuous skill refinement and assessment. Its design allows for repeated practice without the need for constant replacement of parts, making it a cost-effective solution for long-term training programs. Educators can use the simulator to assess learners' progress objectively, identifying areas for improvement and tailoring further training. This ongoing assessment and practice capability ensures that gastroenterology trainees can consistently refine their techniques, leading to improved procedural outcomes in clinical settings.
Integrating Simulation-Based Training into Clinical Programs
Bridging Theoretical Knowledge and Practical Skills
Integrating the ERCP Simulator II into clinical programs creates a seamless bridge between theoretical knowledge and practical application. Traditional gastroenterology education often relies heavily on textbook learning and observational experiences. However, the simulator provides a hands-on approach that allows trainees to apply their theoretical understanding in a controlled environment. This integration helps solidify concepts learned in lectures and demonstrations, making the learning process more engaging and effective. As trainees manipulate the endoscope and navigate through the simulated anatomy, they gain a deeper understanding of spatial relationships and procedural nuances that are difficult to grasp from textbooks alone.
Standardizing Training Protocols
The ERCP Simulator II plays a pivotal role in standardizing training protocols across different medical institutions. By providing a consistent and reproducible training platform, it ensures that all trainees receive uniform exposure to various ERCP scenarios and techniques. This standardization is crucial in maintaining high-quality education and preparing gastroenterology professionals who can deliver consistent care regardless of their training background. Institutions can develop structured curricula around the simulator, incorporating it into various stages of medical education, from undergraduate programs to advanced fellowship training.
Enhancing Patient Safety through Pre-Clinical Practice
Perhaps the most significant impact of integrating the ERCP Simulator II into clinical programs is the enhancement of patient safety. By allowing trainees to practice and perfect their techniques in a risk-free environment, the simulator significantly reduces the potential for errors during actual patient procedures. This pre-clinical practice is especially crucial for complex procedures like ERCP, where the stakes are high, and the margin for error is small. Trainees can encounter and learn to manage various complications in a controlled setting, preparing them for real-world scenarios without putting patients at risk. This approach aligns with the growing emphasis on patient safety in medical education and practice.
Enhancing Learner Confidence and Procedural Readiness
Building Confidence Through Repeated Practice
The ERCP Simulator II serves as an invaluable tool in building learner confidence. The ability to practice procedures repeatedly without the pressure of a real clinical setting allows trainees to become comfortable with the equipment and techniques involved in ERCP. This repeated exposure helps reduce anxiety and improves manual dexterity, leading to increased confidence when performing actual procedures. As learners progress from basic to more complex scenarios on the simulator, they develop a sense of mastery that translates into greater self-assurance in clinical environments. This confidence is crucial in gastroenterology, where procedural competence often correlates with better patient outcomes and reduced complication rates.
Accelerating the Learning Curve
One of the most significant advantages of the ERCP Simulator II is its ability to accelerate the learning curve for gastroenterology trainees. Traditional learning methods often require extended periods of observation before hands-on experience can be gained. In contrast, the simulator allows for immediate and repeated hands-on practice. This accelerated approach enables trainees to gain proficiency in ERCP techniques more rapidly than through conventional training alone. The simulator's various difficulty levels and customizable scenarios ensure that learners can progressively challenge themselves, continually pushing the boundaries of their skills and knowledge. This efficient learning process is particularly beneficial in today's fast-paced medical education environment, where time constraints are often a significant challenge.
Preparing for Real-World Procedural Challenges
The ERCP Simulator II excels in preparing learners for real-world procedural challenges. Its high-fidelity design, which includes realistic anatomical variations and potential complications, provides a comprehensive training experience. Trainees can encounter and learn to manage various scenarios they might face in clinical practice, such as difficult cannulations, unexpected anatomical variations, or complications like bleeding or perforation. This exposure to a wide range of potential situations enhances procedural readiness, ensuring that when faced with similar challenges in real patients, trainees are better prepared to respond effectively. The simulator's ability to replicate these complex scenarios repeatedly allows for the development of critical thinking and decision-making skills essential in gastroenterology procedures.
Conclusion
The ERCP Simulator II stands as a cornerstone in modern gastroenterology education. Its integration into medical curricula represents a significant leap forward in preparing the next generation of endoscopists. By providing a realistic, versatile, and safe environment for skill development, it addresses the critical need for hands-on experience without compromising patient safety. As medical education continues to evolve, the role of advanced simulators like the ERCP Simulator II will undoubtedly expand, shaping more competent, confident, and patient-focused healthcare professionals in the field of gastroenterology.
Contact Us
Elevate your gastroenterology training program with Trandomed's ERCP Simulator II. Experience the benefits of cutting-edge simulation technology, customizable training scenarios, and unparalleled anatomical accuracy. For more information on how our ERCP Simulator II can transform your medical education curriculum, contact us at jackson.chen@trandomed.com. Take the next step in revolutionizing endoscopic training and enhancing patient care.